At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Salesforce B2C-Solution-Architect exam questions by Salesforce. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Salesforce Certified B2C Solution Architect exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Salesforce in their Salesforce B2C-Solution-Architect exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Salesforce Certified B2C Solution Architect exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Salesforce B2C-Solution-Architect exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
A company wants to use Marketing Cloud to send customer electronic receipts that originate from its point of sale (POS) system. The company has a need for the receipt to be sent no more than 10 minutes after purchase and would like to track all email sends that are being placed to that customer, The Marketing Cloud Contact Key should be the Service Cloud Contact ID.
What solution should a Solution Architect recommend to achieve this need?
A global merchant plans to use B2C Commerce, Service Cloud, and Marketing Cloud to support the shopper experience. They also plan on using Marketing Cloud Connect to integrate Service and Marketing Clouds and the Service Cloud Connector for B2C Commerce. The customers will receive SMS messages through Mobile Connect. One of the key requirements is to enable consent and profile management across the clouds.
Which two recommendations should a Solution Architect make as part of the solution?
Choose 2 answers
A) SMS opt-in will sync with Service Cloud when contact ID is the subscriber key in Marketing Cloud. This can help enable consent and profile management across the clouds by allowing customers to opt-in or opt-out of SMS messages and reflecting their preferences in both Service Cloud and Marketing Cloud. This can also help comply with industry regulations and best practices for SMS marketing. C. Profile changes in B2C Commerce will sync to Service Cloud when person accounts are used. This can help enable consent and profile management across the clouds by allowing customers to update their profile information in B2C Commerce and syncing their changes to Service Cloud. This can also help maintain consistent and accurate customer data across different systems and platforms. Reference:
https://help.salesforce.com/s/articleView?id=sf.mc_co_person_accounts.htm&type=5
https://help.salesforce.com/s/articleView?id=sf.mc_co_implement_marketing_cloud_connect.htm&type=5
https://help.salesforce.com/s/articleView?id=sf.b2c_commerce_integration.htm&type=5
An ecommerce company has one B2C Commerce Primary Instance Group with three storefronts and is considering Marketing Cloud for email messaging and customer journey orchestration. The company has a strong desire to implement product recommendations in their email messaging as well as implement the abandoned cart use-case.
Which two approaches should a Solution Architect recommend to ensure that the company can implement solutions that align with their requirements?
Choose 2 answers
Refer to the exhibit.
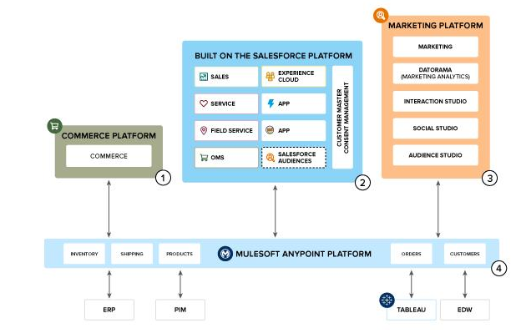
A company plans to adopt Salesforce for a number of their needs, including an internal CRM, a public B2C Commerce storefront with order management functionality, and an extensible API framework to integrate with other systems, as well as marketing automation. The overall system landscape of the proposed solution is shown above.
Which three considerations are important for this scenario? Choose 3 answers
Option A is correct because the Salesforce Platform can be used for customer master and consent management, or it can integrate with a third-party Master Data Management system. This is an important consideration for this scenario, as it affects the data quality, security, and governance of customer data across multiple Salesforce clouds and systems.
Option C is correct because Order Management System (OMS) is a B2C Commerce product but it does not run natively on the core Salesforce Platform. This is an important consideration for this scenario, as it affects the integration, performance, and scalability of OMS with other Salesforce clouds and systems.
Option D is correct because Marketing Cloud enables personalization, journey orchestration, and cross-channel messaging. This is an important consideration for this scenario, as it affects the marketing strategy, campaign design, and customer engagement of the company.
Option B is incorrect because Tableau does not require MuleSoft in order to access data outside of the Salesforce Platform. Tableau can connect to various data sources using native connectors or custom connectors without relying on MuleSoft.
[Get Started with B2C Solution Architect Cert Prep - Trailhead]
[Certification - B2C Solution Architect - Trailhead]
An organization wants to avoid sending post-purchase review emails until a customer has had a chance to receive and try out their order. The typical shipping duration is around 3 days, but the organization is unsure about how long it takes a customer to try the product once it has been delivered.
What should the company do to leverage its Salesforce product suite and optimize the open rates for its post-purchase emails?