At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Pure Storage FAAA_004 exam questions by Pure Storage. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Pure Storage FlashArray Architect Associate exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Pure Storage in their Pure Storage FAAA_004 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Pure Storage FlashArray Architect Associate exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Pure Storage FAAA_004 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
What metric is used to compute billing when customers leverage the Evergreen//One offering?
When customers leverage the Evergreen//One offering , billing is based on the effective capacity consumed .
Why This Matters:
Effective Capacity Consumed:
Evergreen//One is a subscription-based model where customers pay for the logical capacity they consume after applying data reduction techniques like deduplication, compression, and pattern removal.
This ensures customers only pay for the actual usable capacity they need, aligning with Pure Storage's commitment to delivering predictable and cost-effective storage solutions.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . Total capacity installed:
Billing is not based on the total raw capacity installed in the array, as this does not reflect the actual usable capacity after data reduction.
B . Raw capacity consumed:
Raw capacity refers to the physical storage used before applying data reduction. Evergreen//One focuses on effective capacity, not raw capacity.
D . Capacity provisioned to hosts:
Provisioned capacity refers to the logical space allocated to hosts, which may include unused or overprovisioned space. Billing is based on the actual consumed capacity.
Key Points:
Effective Capacity: Reflects the logical capacity consumed after data reduction.
Subscription Model: Aligns with Evergreen//One's focus on predictable and flexible billing.
Data Reduction: Deduplication, compression, and pattern removal optimize storage efficiency, reducing costs for customers.
Pure Storage Evergreen//One Documentation: 'Understanding Billing Metrics'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Maximizing Value with Evergreen Subscriptions'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'How Evergreen//One Billing Works'
What causes a disruption to Pure FlashArray stateless controller operations or performance, if there is a single array?
Among the listed options, physically relocating an array is the action most likely to cause a disruption to Pure FlashArray stateless controller operations or performance.
Why This Matters:
Physical Relocation:
Moving a FlashArray involves powering down the system, disconnecting cables, and transporting the hardware to a new location. This process inherently disrupts operations and performance until the array is reinstalled and brought back online.
Even with proper planning, physical relocation introduces downtime and potential risks (e.g., hardware damage during transport).
Why Not the Other Options?
A . Replacing a controller I/O module:
FlashArray controllers are designed with redundancy and hot-swappable components. Replacing an I/O module typically does not cause significant disruptions, as the other controller continues to handle operations.
C . Moving from a SAS- to NVMe-based shelf:
Transitioning to NVMe-based shelves is a planned upgrade that does not inherently disrupt operations. The array can continue functioning during the transition, though performance may vary temporarily.
D . Upgrade Purity//FA code:
Upgrading Purity//FA (the operating system for FlashArray) is a non-disruptive process. FlashArray supports rolling upgrades, ensuring continuous availability and performance during the update.
Key Points:
Physical Relocation: Causes unavoidable downtime and operational disruption.
Redundancy and Non-Disruptive Operations: FlashArray is designed to minimize disruptions for tasks like module replacement and software upgrades.
Planning Required: Physical relocation requires careful planning to minimize risks and downtime.
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: 'Maintenance and Relocation Best Practices'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Non-Disruptive Operations with FlashArray'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Minimizing Disruptions During Array Maintenance'
What is the minimally required FlashArray model that includes the DirectCompress Accelerator (DCA)?
The DirectCompress Accelerator (DCA) is a hardware component introduced in certain FlashArray models to enhance inline data compression performance. To determine the minimally required FlashArray model that includes DCA, let's analyze the options:
Analysis of Options:
A . FlashArray//X70 R4 :
The FlashArray//X70 R4 was the first model to include the DirectCompress Accelerator (DCA).
This makes it the minimally required model for DCA support.
B . FlashArray//X70 R3 :
The FlashArray//X70 R3 does not include the DCA. It relies on software-based compression, which is less efficient than hardware-accelerated compression.
C . FlashArray//X90 R4 :
The FlashArray//X90 R4 includes DCA but is a higher-tier model than the X70 R4. While it supports DCA, it is not the minimal requirement.
D . FlashArray//XL130 :
The FlashArray//XL130 is a high-performance model that includes DCA, but it is overkill for this requirement and not the minimal model.
Recommendation:
The correct answer is A. FlashArray//X70 R4 , as it is the first model to include the DirectCompress Accelerator (DCA).
FlashArray Hardware Specifications :
Details the features and capabilities of each FlashArray model.
DirectCompress Accelerator Overview :
Explains the benefits and availability of DCA.
The customer asks if the FlashArray is suitable for a cloud-native application that utilizes containers and Kubernetes. Which response addresses this question?
The FlashArray is suitable for cloud-native applications that utilize containers and Kubernetes, but the best way to address this use case is through Pure Storage's Portworx offering .
Why This Matters:
Portworx:
Portworx is a container storage and data management platform specifically designed for Kubernetes and cloud-native applications. It integrates seamlessly with FlashArray to provide persistent storage, data protection, and advanced features like snapshots, replication, and disaster recovery for containerized workloads.
Portworx ensures high performance, scalability, and reliability for stateful applications running in Kubernetes environments.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . This is not supported with FlashArray and this application data will need to be stored on a different array:
This statement is incorrect. FlashArray is fully capable of supporting cloud-native applications when paired with the right tools, such as Portworx.
B . This is supported via an installable CSI provider specifically for the FlashArray:
While FlashArray does support a Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver, it is a basic integration and does not provide the advanced features and capabilities offered by Portworx for Kubernetes environments.
D . This is supported and Pure uses a software layer that is only compatible with DAS storage in Kubernetes:
This statement is incorrect. Pure Storage solutions are compatible with both direct-attached storage (DAS) and external storage arrays like FlashArray.
Key Points:
Portworx: The recommended solution for integrating FlashArray with Kubernetes and containerized applications.
Advanced Features: Provides persistent storage, data protection, and scalability for cloud-native workloads.
Integration: Ensures seamless compatibility between FlashArray and Kubernetes environments.
Pure Storage Portworx Documentation: 'Integrating Portworx with FlashArray'
Pure Storage Whitepaper: 'Cloud-Native Storage Solutions with Portworx'
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: 'Best Practices for Kubernetes and FlashArray Integration'
Refer to the exhibit.
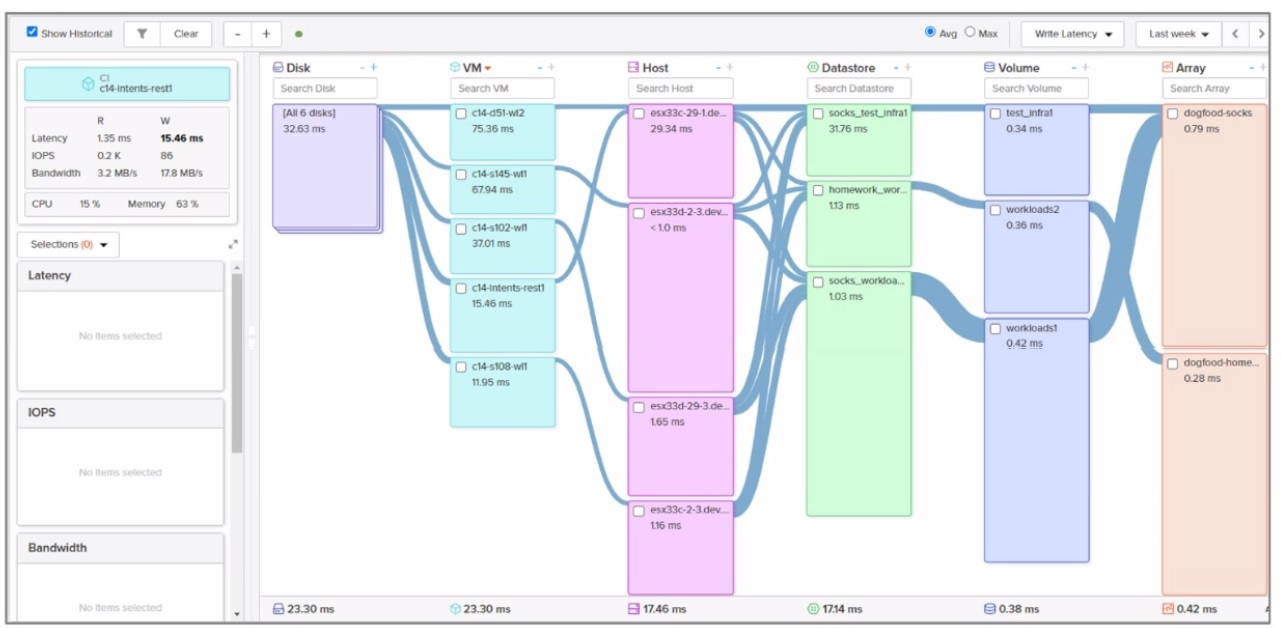
Which VM is running on the ESXi host with the lowest write latency?
Write Latency:
Write latency refers to the time it takes for a write operation to complete on the storage array. Lower write latency indicates better performance and faster response times for write-intensive workloads.
In Pure Storage arrays, write latency is typically measured in milliseconds (ms) and can be monitored using tools like Pure1 or Purity//FA performance metrics.
VM-to-Host Mapping:
Each VM runs on an ESXi host, and the write latency of the VM is influenced by the storage performance characteristics of the host it resides on.
To identify the VM with the lowest write latency, we must compare the write latency values for each VM listed in the exhibit.