At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Pegasystems PEGAPCDC87V1 exam questions by Pegasystems. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Pegasystems Certified Pega Decisioning Consultant (PCDC) 87V1 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Pegasystems in their Pegasystems PEGAPCDC87V1 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Pegasystems Certified Pega Decisioning Consultant (PCDC) 87V1 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Pegasystems PEGAPCDC87V1 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
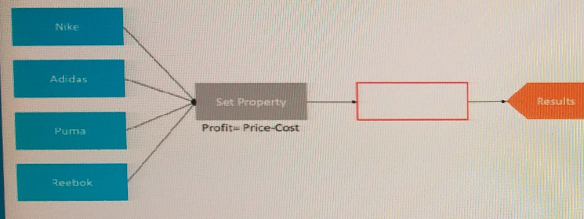
The following decision strategy outputs the most profitable shoe a retailer can sell. The profit is the selling Price of the shoe, minus the Cost to acquire the shoe.
The details of the shoes are provided in the following table:

What is the number of outputs that each component has?
Set-Property Component: This component performs the calculation of profit for each of the four brands (Nike, Adidas, Puma, Reebok). Since the Set-Property component is configured to calculate profit for each brand individually, it processes four inputs, resulting in four outputs.
Results Component: This component collects the outputs from the Set-Property component and simply passes them through, leading to four outputs.
Thus, both components handle and produce outputs corresponding to each brand processed, which are four in total
A bank is currently sending promotional emails related to credit card offers to qualified customers. Now the bank wants to prevent overexposure to these offers. As a part of this effort, the bank wants to avoid sending the same promotional offer email for the next 60 days if the email was rejected twice by the customer in the last 30 days. How do you define the suppression rule for this contact policy?
To prevent overexposure and avoid sending the same promotional offer email for the next 60 days if the email was rejected twice by the customer in the last 30 days, you should define the suppression rule as 'Suppress an action for 60 days if there are 2 rejects in the email channel in the last 30 days.' This rule ensures that specific actions are paused based on the customer's past interaction history, preventing repetitive and potentially annoying communications.
Configuring contact policies and suppression rules (Page 66-67)
Reference module: Testing engagement policy conditions using audience simulation
U+ Bank, a retail bank, recently implemented a project in which credit card offers are presented to qualified customers when the customers log in to the web self-service portal. The bank now plans to amend its engagement policy conditions. As a Decisioning Consultant, which simulation do you run to check if the conditions are too broad or narrow for your requirements?
Identifying the Requirement:
The bank has chosen an email service provider that prefers receiving customer batches through a cloud storage location on either Microsoft Azure or Amazon S3.
The task is to find out how Pega Customer Decision Hub can integrate with these cloud storage solutions.
Evaluating Pega CDH Capabilities:
Pega Customer Decision Hub provides robust capabilities for integrating with various external systems and cloud storage solutions.
The documentation for Pega CDH supports writing action details directly to cloud storage solutions like Microsoft Azure and Amazon S3, which is in line with modern cloud infrastructure practices.
Process Overview:
Configuration:
Configure the external storage location (Azure Blob Storage or Amazon S3) within Pega CDH.
Action Flow:
Define the action flow to include steps for writing data to the specified cloud storage.
External Integration:
Use built-in connectors or custom integration points to handle data transfer securely and efficiently.
Reference and Supporting Documentation:
According to the Pega Customer Decision Hub User Guide, you can configure Pega CDH to write action details directly to cloud storage solutions like Microsoft Azure and Amazon S3 (refer to the section on configuring the delivery of multiple treatments and external integration points).
Pega-Customer-Decision-Hub-User-Guide-85.pdf
Pega-Customer-Decision-Hub-User-Guide-86.pdf
Pega-Customer-Decision-Hub-User-Guide-87.pdf
Reference module: Essentials of always-on outbound
A bank has been running traditional marketing campaigns for many years. One such campaign sends an offer email to qualified customers on day 1. On day 3, it sends a reminder email to customers who haven't responded to the first email. On day 7, it sends a second reminder to customers who haven't responded to the first two emails. If you were to re-implement this requirement using the always-on outbound customer engagement paradigm, how would you approach this scenario?
To re-implement the bank's traditional marketing campaign using the always-on outbound customer engagement paradigm in Pega, follow these steps:
Understand the Traditional Campaign Requirements:
Day 1: Send an offer email to qualified customers.
Day 3: Send a reminder email to customers who haven't responded to the first email.
Day 7: Send a second reminder to customers who haven't responded to the first two emails.
Set Up Next-Best-Action Designer:
Use the Next-Best-Action Designer to define engagement policies, arbitration, and channels to manage customer interactions.
The always-on approach continuously evaluates customer interactions and selects the best action based on real-time data and AI-driven insights.
Configure the Primary Schedule:
Set up a daily run schedule for the Next-Best-Action strategy. This allows the AI to evaluate customer interactions daily and decide the best action to take.
Leverage AI for Decisioning:
Configure the AI models to determine the best action for each customer based on their interaction history and engagement policies. The AI will automatically handle:
Sending the initial offer email on Day 1.
Sending a reminder email on Day 3 to those who haven't responded.
Sending a second reminder on Day 7 to those who still haven't responded.
Define Engagement Policies:
Eligibility: Define which customers qualify for the offer.
Applicability: Ensure the offer is relevant to the customer.
Suitability: Verify that sending the offer is in the best interest of the customer.
Contact Policies: Set rules to manage the frequency and timing of emails to avoid over-communication.
Implement AI-Driven Actions:
Use the Next-Best-Action strategy framework to select actions (e.g., sending emails) based on the AI model's recommendations.
Configure treatments (email content) and channels (email) within the Next-Best-Action Designer.
Monitor and Adjust:
Continuously monitor the performance of the campaign using Pega's analytics and adjust the strategy as needed to optimize engagement and response rates.
Pega Customer Decision Hub User Guide 8.5: Understanding Next-Best-Action Designer basics, Configuring the Next-Best-Action Designer for Pega Customer Service, Setting constraints contact policy limits and controls.
MyCo, a telecom company, wants to present their customers on Facebook with customer-centric mobile internet offers. What action must MyCo take to meet this business requirement?
To present customer-centric mobile internet offers on Facebook, MyCo should place a paid ad. This action ensures that the offers are targeted and displayed to the relevant audience on the social media platform, leveraging Pega Customer Decision Hub's integration with paid media channels like Facebook Ads.