At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the PECB ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor exam questions by PECB. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the PECB QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by PECB in their PECB ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their PECB QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the PECB ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
You, as auditor, are in dialogue with the quality lead and managing director of a small business that supplies specialist laboratory equipment and furniture.
You: "I'd like to look at how you manage change in the organisation. What changes have you made as a
business, say, over the last 12 months?"
Auditee: "We have made some strategic changes, the main one being that we no longer manufacture our
own products in house."
You: "That sounds like quite a significant change. What has been the impact of that?"
Auditee: "We now mainly sell other manufacturers' products, under their brand names, and have outsourced
manufacture of our own brand products to one of our suppliers. Unfortunately, we had to make six members
of our staff redundant. This represents about 20% of our workforce, so this has been quite a challenging
time."
You: "I'm sure. What were the reasons for making the change?"
Auditee: "Our manufacturing section was a small operation, and we struggled to cope with fluctuations in
demand. During busy periods, we found it hard to meet lead times, and in quiet periods we had staff with
little to do. This was having an impact on customer satisfaction and meant we had to charge premium prices
that made our product uncompetitive."
You: "How did you go about the change?"
The auditor asks to speak to the purchasing manager about the selection of the subcontractor to
manufacture the company's own brand products.
You: "How did you choose a supplier to manufacture your products?"
Auditee: "We have had a long-term relationship with a supplier ABC Ltd - we gave them our design
drawings, got them to complete a supplier questionnaire and run a couple of trial batches for us. We were
happy with the result and we have used them ever since."
ISO 9001:2015, clause 8.4.1 outlines situations when controls need to be applied to externally provided processes, products and services. Which one of the following situations is applicable to this scenario?
According to the ISO 9001:2015 standard, clause 8.4.1 requires organizations to ensure that externally provided processes, products and services conform to requirements. Controls must be applied to externally provided processes, products and services when:
The products and services are intended for incorporation into the organization's own products and services.
They are provided directly to customers by the external provider on behalf of the organization.
A process, or part of a process, is provided by an external provider as a result of a decision by the organization.
In this scenario, the auditee has chosen a supplier to manufacture their own brand products based on their design drawings, supplier questionnaire and trial batches. This means that the supplier is providing a process (manufacturing) as a result of a decision by the organization (the auditee). Therefore, clause 8.4.1 applies to this situation.
You are conducting a Stage 1 audit at an organisation that services refrigeration equipment for a large customer base.
The scope of certification is "Provision of refrigeration equipment maintenance and repair services". You are interviewing
the Managing Director to learn more about the organisation and to explore how the requirements for policy, objectives,
and risks and opportunities in ISO 9001 are addressed.
The Managing Director explains that they only use sub-contract refrigeration engineers and do not have any full-time
refrigeration engineers, which helps to optimise overhead costs. The full-time staff employed are essentially a small team
of office staff who process customer enquiries, schedule jobs and process invoices.
The Managing Director adds that the ISO 9001 requirements for competence of personnel extends to both sub-contract
and full-time staff. He also states that the full-time staff are aware of the Quality Policy, objectives and plans to address
risk and opportunities.
You ask if the sub-contract engineers have been informed of the Quality Policy, objectives and plans to address risks and
opportunities, to which the Managing Director replies that this is not applicable as they only use sub-contractors who
operate ISO 9001 certificated quality management systems. The documented information provided to the auditor
confirms this.
Which clause in ISO 9001 is most likely not to have been fulfilled in this instance?
Questions no: 16 Verified Answer: = C. 7.4 Communication Comprehensive But Short = Clause 7.4 of
An audit team of three people is conducting a Stage 2 audit to ISO 9001 of an engineering organisation that manufactures sacrificial anodes for the oll and gas industry in marine environments. These are aluminium products designed to prevent corrosion of submerged
steel structures. You, as one of the auditors, find that the organisation has shipped anodes for Project DK in the Gulf of Mexico before the galvanic efficiency test results for the anodes have been fully analysed and reported as required by the customer. The Quality
Manager explains that the Managing Director authorised release of the anodes to avoid late delivery as penalties would be imposed. The customer was not informed since the tests very rarely fall below the required efficiency. You raise a nonconformity against clause 8.6 of ISO 9001.
Which of the following options for the best description of the nonconformity?
Clause Reference -- ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8.6 (Release of Products and Services): ISO 9001 requires that products and services are not released to the customer until:
All planned verification activities have been completed.
Acceptance criteria have been met.
Any necessary approvals have been obtained.
In this scenario:
The sacrificial anodes for Project DK were shipped before the galvanic efficiency test results were analyzed.
This constitutes a nonconformity against Clause 8.6 because the products were released without completing the required tests.
Option Analysis:
A. A retrospective concession was not sought from the customer once the test results had been approved by the Quality Manager: Incorrect. While obtaining a concession might mitigate the situation, the nonconformity pertains to the process failure of releasing the products without completing required tests, not the absence of a concession.
B. Release of the product without acceptable test results has been accepted by the customer for Project DK: Incorrect. The customer was not informed before the release, and there is no indication that this was accepted beforehand. Furthermore, ISO 9001 requires planned processes to be followed, regardless of later acceptance.
C. Products for Project DK have been released before product approval through the quality control process: Correct. This description accurately reflects the nonconformity. The quality control process required test results to be analyzed and verified before release, which did not happen.
D. The untested product was not recalled until the galvanic efficiency of the anodes was verified: Incorrect. The issue is not about recalling the product but about releasing it without completing the required tests. Recalling the product is not mentioned in the scenario.
Why C is Correct:
The nonconformity is a clear breach of Clause 8.6, where the products were released without meeting the planned verification requirements.
This demonstrates a failure in adhering to quality control processes, which is a critical aspect of ISO 9001 compliance.
Key ISO 9001 Reference:
Clause 8.6: Products and services shall not be released to the customer until all planned activities (e.g., testing) have been satisfactorily completed, or the customer has approved the release with knowledge of deviations.
Which one of the following options is the definition of the context of an organisation?
Understanding 'Context of the Organization': The term 'context of the organization' is defined in ISO 9001:2015 Clause 4.1, which states:
'The organization shall determine external and internal issues that are relevant to its purpose and its strategic direction and that affect its ability to achieve the intended result(s) of its quality management system.'
The definition emphasizes identifying both internal and external issues that influence the organization's approach to developing and achieving its objectives.
Option Analysis:
Option A: Correct. This option aligns with the standard definition as it explicitly mentions the combination of internal and external issues that affect the organization's approach to achieving its objectives, which is the essence of Clause 4.1.
Option B: Incorrect. The term 'comparison of internal and external issues' does not reflect the ISO 9001 requirements. The standard does not require a comparison but rather an understanding of these issues.
Option C: Incorrect. Although it mentions 'complexity,' the focus of ISO 9001:2015 is on identifying relevant issues rather than the complexity of those issues.
Option D: Incorrect. This option mentions 'coordination' and focuses only on the positive or negative effects. ISO 9001 requires identifying issues but does not emphasize coordination.
Clause Reference and Relevance: ISO 9001:2015 requires organizations to understand their context because internal and external factors can influence the Quality Management System's effectiveness. Understanding this context helps in:
Addressing risks and opportunities (Clause 6.1).
Aligning the QMS with the organization's strategic direction.
Why A is Correct: 'Combination of internal and external issues' captures the essence of Clause 4.1, making it the accurate definition of the context of the organization.
XYZ Corporation is an organisation that employs 100 people. As audit team leader, you are conducting a
certification audit at Stage 1. When reviewing the quality management system (QMS) documentation, you
find that quality objectives have been set for every employee in the organisation except top management.
The Quality Manager complains that this has created a lot of resistance to the QMS, and the Chief Executive
is asking questions about how much it will cost. He asks for your opinion on whether this is the correct
method of setting objectives.
Three months after Stage 1, you return to XYZ Corporation to conduct a Stage 2 certification audit as Audit
Team Leader with one other auditor. You find that the Quality Manager has cancelled the previous quality
objectives for all employees and replaced them with a single objective for himself. This states that "The
Quality Manager will drive multiple improvements in the QMS in the next year". The Quality Manager indicates
that this gives him the authority to issue instructions to department managers when quality improvement is
needed. He says that this approach has the full backing of senior management. He shows you the latest
Quality Improvement Request that was included in the last management review.
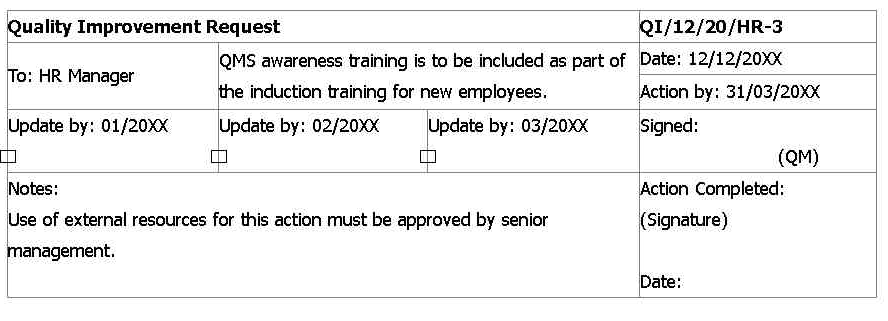
After further auditing, the issues below were found. Select two statements that apply to the term
`nonconformity'.
According to the ISO 9001:2015 standard, clause 10.2.1 defines nonconformity as the non-fulfilment of a requirement. A requirement can be related to the quality management system, the products and services, the customer expectations, or the applicable statutory and regulatory requirements. Nonconformities can be detected through various sources, such as audits, inspections, tests, customer complaints, or internal reviews. Nonconformities must be addressed by taking appropriate actions to correct them and prevent their recurrence.
In this scenario, the auditee has shown several issues that indicate nonconformities in their quality management system. Two statements that apply to the term nonconformity are:
A . No quality objectives planned for the top management team:According to ISO 9001, clause 6.2.1, the organization must establish quality objectives at relevant functions, levels, and processes. The quality objectives must be consistent with the quality policy and the strategic direction of the organization. The top management team is responsible for providing leadership and direction for the quality management system and ensuring its alignment with the organization's purpose and context. Therefore, the absence of quality objectives for the top management team is a nonconformity as it violates the requirement of clause 6.2.1.
E . Quality improvements not aligning with the quality policy:According to ISO 9001, clause 5.2.1, the quality policy is a statement of the organization's intentions and direction regarding quality, as formally expressed by top management. The quality policy must provide a framework for setting quality objectives and be compatible with the context and strategic direction of the organization. The quality policy must also be communicated, understood, and applied within the organization. Therefore, if the quality improvements are not aligned with the quality policy, it is a nonconformity as it violates the requirement of clause 5.2.1.