At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the LPI 102-500 exam questions by LPI. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the LPIC-1 System Administrator Exam 102, Part 2 of 2, version 5.0 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by LPI in their LPI 102-500 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their LPIC-1 System Administrator Exam 102, Part 2 of 2, version 5.0 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the LPI 102-500 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
What is the top-level directory which contains the configuration files for CUPS? (Specify the full path to the directory.)
Which of the following SQL statements will select the fields name and address from the contacts table?
Which of the following statements is true if the UID of a regular user is identical to the GID of a group?
Which file contains a set of services and hosts that will be allowed to connect to the server by going through a TCP Wrapper program such as tcpd? (Specify the full name of the file, including path.)https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-5cd-clmKnbk/AAAAAAAAAAI/AAAAAAAAADM/-SXesH19Ido/s46-c-k-no/photo.jpg
The /etc/hosts.allow file contains a set of rules that specify which services and hosts are allowed to connect to the server by going through a TCP Wrapper program such as tcpd. TCP Wrappers are a security mechanism that can filter incoming requests based on the source address, destination address, and service name. TCP Wrappers can also perform logging, redirection, and execution of commands based on the rules.
The /etc/hosts.allow file has the following format:
service_list : host_list [ : option_list ]
The service_list is a comma-separated list of service names, such as sshd, telnet, or ftp. The host_list is a comma-separated list of host names, IP addresses, or network masks that are allowed to access the services. The option_list is an optional list of keywords that can modify the behavior of the rule, such as twist, spawn, deny, or allow.
For example, the following rule in /etc/hosts.allow allows ssh access from any host in the 192.168.1.0/24 network, and logs the connection attempt:
sshd : 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0 : spawn /bin/echo %a from %h attempted to access %d >> /var/log/sshd.log
The /etc/hosts.allow file is processed before the /etc/hosts.deny file, which contains the rules for denying access to the server. If a request matches a rule in /etc/hosts.allow, it is granted access and the processing stops. If it does not match any rule in /etc/hosts.allow, it is checked against the rules in /etc/hosts.deny. If it matches a rule in /etc/hosts.deny, it is denied access and the processing stops. If it does not match any rule in either file, it is granted access by default.
LPI 102-500 Exam Objectives, Topic 110.3: Implement host security
LPI 102-500 Study Guide, Chapter 10: Securing Your System, Section 10.3: TCP Wrappers
Which of Ihe following commands sets the system's time zone to the Canadian Eastern Time?
A)

B)
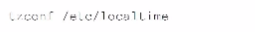
C)
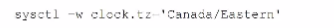
D)

E)
