At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Juniper JN0-683 exam questions by Juniper. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Juniper Data Center Professional exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Juniper in their Juniper JN0-683 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Juniper Data Center Professional exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Juniper JN0-683 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Exhibit.
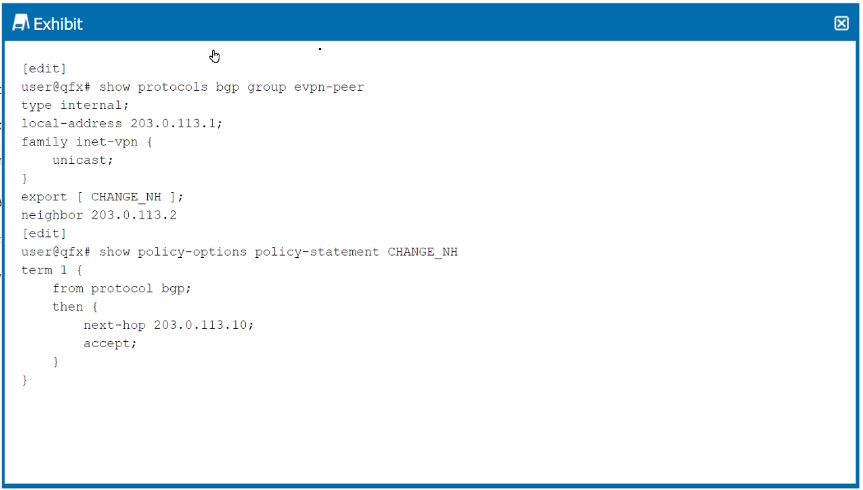
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, why has the next hop remained the same for the EVPN routes advertised to the peer 203.0.113.2?
Understanding the Configuration:
The configuration shown in the exhibit involves an EVPN (Ethernet VPN) setup using BGP as the routing protocol. The export policy named CHANGE_NH is applied to the BGP group evpn-peer, which includes a rule to change the next hop for routes that match the policy.
Issue with Next Hop Not Changing:
The policy CHANGE_NH is correctly configured to change the next hop to 203.0.113.10 for the matching routes. However, the next hop remains unchanged when advertising EVPN routes to the peer 203.0.113.2.
Reason for the Issue:
In Junos OS, when exporting routes for VPNs (including EVPN), the next-hop change defined in a policy will not take effect unless the vpn-apply-export parameter is used in the BGP configuration. This parameter ensures that the export policy is applied specifically to VPN routes.
The vpn-apply-export parameter must be included to apply the next-hop change to EVPN routes.
Correct Answer Explanation:
D . The vpn-apply-export parameter must be applied to this peer: This is the correct solution because the next hop in EVPN routes won't be altered without this parameter in the BGP configuration. It instructs the BGP process to apply the export policy to the EVPN routes.
Data Center Reference:
This behavior is standard in EVPN deployments with Juniper Networks devices, where the export policies applied to VPN routes require explicit invocation using vpn-apply-export to take effect.
As part of the onboarding process for new switches being added to your data centers, your company uses Juniper Networks' ZTP process. As part of the ZTP process, a script is executed by the devices being onboarded.
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP):
Juniper Networks' ZTP (Zero Touch Provisioning) process automates the deployment of new devices by allowing them to fetch and execute scripts for configuration and setup as they are powered on and connected to the network.
Supported Scripting Languages:
The Junos OS supports several scripting languages that can be used during the ZTP process:
Shell scripts are often used for general automation tasks.
Python is a widely supported language in Junos, offering powerful scripting capabilities for automating network tasks.
SLAX (Service Logic Execution Environment) is a scripting language specific to Junos, designed to automate configuration tasks and simplify network operations.
Conclusion:
Option D: Correct---Junos ZTP supports Shell, Python, and SLAX, making it the correct choice among the provided options.
In your EVPN-VXAN environment, you want to prevent a multihomed server from receiving multiple copies of BUM traffic in active/active scenarios. Which EVPN route type would satisfy this requirement?
Understanding the Scenario:
In an EVPN-VXLAN environment, when using multi-homing in active/active scenarios, there's a risk that a multihomed server might receive duplicate copies of Broadcast, Unknown unicast, and Multicast (BUM) traffic. This is because multiple VTEPs might forward the same BUM traffic to the server.
EVPN Route Types:
Type 4 Route (Ethernet Segment Route): This route type is used to advertise the Ethernet Segment (ES) to which the device is connected. It is specifically used in multi-homing scenarios to signal the ES and its associated Ethernet Tag to all the remote VTEPs. The Type 4 route includes information that helps prevent BUM traffic duplication in active/active multi-homing by using a split-horizon mechanism, which ensures that traffic sent to a multihomed device does not get looped back.
The Type 4 route is crucial for ensuring that in a multi-homed setup, particularly in an active/active configuration, BUM traffic does not result in duplication at the server. The route helps coordinate which VTEP is responsible for forwarding the BUM traffic to the server, thereby preventing duplicate traffic.
Data Center Reference:
Type 4 routes are essential for managing multi-homing in EVPN to avoid the issues of BUM traffic duplication, which could otherwise lead to inefficiencies and potential network issues.
You want to ensure that VXLAN traffic from the xe-0/0/12 interlace is being encapsulated by logical vlep.32770 and sent to a remote leaf device in this scenario, which command would you use to verify that traffic is flowing?
VXLAN Traffic Verification:
To ensure VXLAN traffic from the xe-0/0/12 interface is correctly encapsulated by the logical vtep.32770 and sent to a remote leaf device, it is essential to monitor the relevant interface statistics.
The command show interfaces terse vtep.32770 statistics provides a concise overview of the traffic statistics for the specific VTEP interface, which can help verify whether traffic is being correctly encapsulated and transmitted.
This command is particularly useful for quickly checking the traffic counters and identifying any potential issues with VXLAN encapsulation or transmission.
It allows you to confirm that traffic is flowing as expected, by checking the transmitted and received packet counters.
Data Center Reference:
Monitoring interface statistics is a crucial step in troubleshooting and validating network traffic, particularly in complex overlay environments like EVPN-VXLAN.
Which three statements are correct about VXLAN control planes? (Choose three.)
VXLAN Control Planes:
VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) uses different control planes to handle MAC learning and traffic forwarding. The control planes include multicast and EVPN (Ethernet VPN).
Multicast and EVPN Comparison:
Option B: Both multicast and EVPN can be used for MAC learning in a VXLAN environment. Multicast is a more traditional approach, while EVPN is more advanced and supports distributed MAC learning.
Option D: EVPN offers benefits such as fast convergence and rapid updates, making it more efficient and scalable for modern data center environments.
Option E: Multicast does not require as many resources because it relies on traditional Layer 3 multicast mechanisms to distribute broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) traffic. However, it can be less flexible and less scalable compared to EVPN.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct---Both control planes facilitate MAC learning.
Option D: Correct---EVPN provides fast convergence and updates.
Option E: Correct---Multicast is resource-efficient but less flexible.