At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Juniper JN0-664 exam questions by Juniper. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Juniper Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Juniper in their Juniper JN0-664 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Juniper Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Juniper JN0-664 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Exhibit
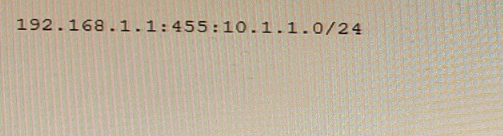
You are examining an L3VPN route that includes the information shown in the exhibit
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
Type 1: When Type value is 1, the Administrator field is 4-bytes and Assigned Number field is 2-bytes. The Administrator field should be set to the IP address (public IP addresses should be used). The Assigned Number field contains a number from a numbering space that is administered by the enterprise to which the IP address has been assigned by the appropriate authority.
Exhibit
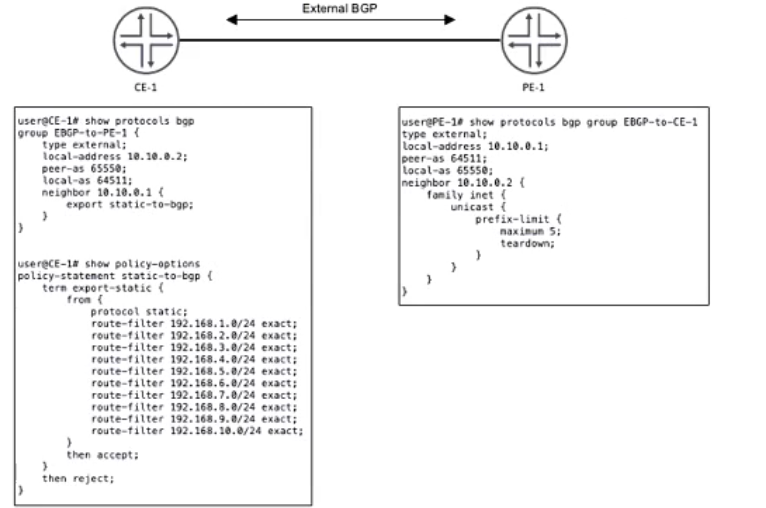
CE-1 must advertise ten subnets to PE-1 using BGP Once CE-1 starts advertising the subnets to PE-1, the BGP peering state changes to Active.
Referring to the CLI output shown in the exhibit, which statement is correct?
Analyzing the Exhibit and Understanding the Issue
The exhibit shows BGP configurations on CE-1 and PE-1, which are connected via EBGP.
CE-1 (Customer Edge)
Uses AS 64511 and establishes an EBGP session with PE-1 (AS 65550).
Configured to export 10 static routes (192.168.1.0/24 - 192.168.10.0/24) using the static-to-bgp policy.
PE-1 (Provider Edge)
Uses AS 65550 and is peering with CE-1 (AS 64511).
Configured with a prefix-limit of 5 on received routes from CE-1.
Teardown enabled, meaning if more than 5 prefixes are received, the BGP session is shut down.
Identifying the Problem
CE-1 is correctly configured with peer AS 65550, so Option B ('CE-1 is configured with an incorrect peer AS') is incorrect .
CE-1 is advertising exactly 10 static routes (as per policy).
PE-1 has a prefix-limit maximum 5 with teardown enabled.
This means that when CE-1 advertises more than 5 prefixes, PE-1 shuts down the BGP session.
BGP moves to the 'Active' state, indicating that the session has been disrupted and PE-1 is trying to re-establish the connection.
CE-1 is reachable since the session was initially established before the limit was exceeded, so Option D ('CE-1 is unreachable') is incorrect .
CE-1 is not advertising its entire routing table, only the static prefixes listed in the policy, so Option A ('CE-1 is advertising its entire routing table') is incorrect .
Correct Answer
C. The prefix limit has been reached on PE-1
Verification from Juniper Documentation
Juniper BGP Prefix Limit Documentation confirms that exceeding the prefix limit with teardown causes the BGP session to go into 'Active' state.
Juniper Troubleshooting Guide for BGP Peering Issues states that when a BGP session reaches the prefix limit and has teardown enabled, the session is terminated.
Exhibit
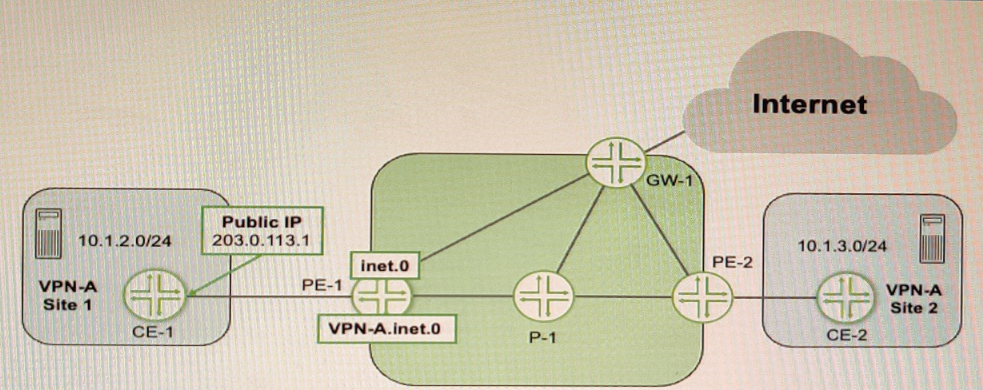
Referring to the exhibit, CE-1 is providing NAT services for the hosts at Site 1 and you must provide Internet access for those hosts
Which two statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
You are configuring a BGP signaled Layer 2 VPN across your MPLS enabled core network. In this scenario, which statement is correct?
Exhibit
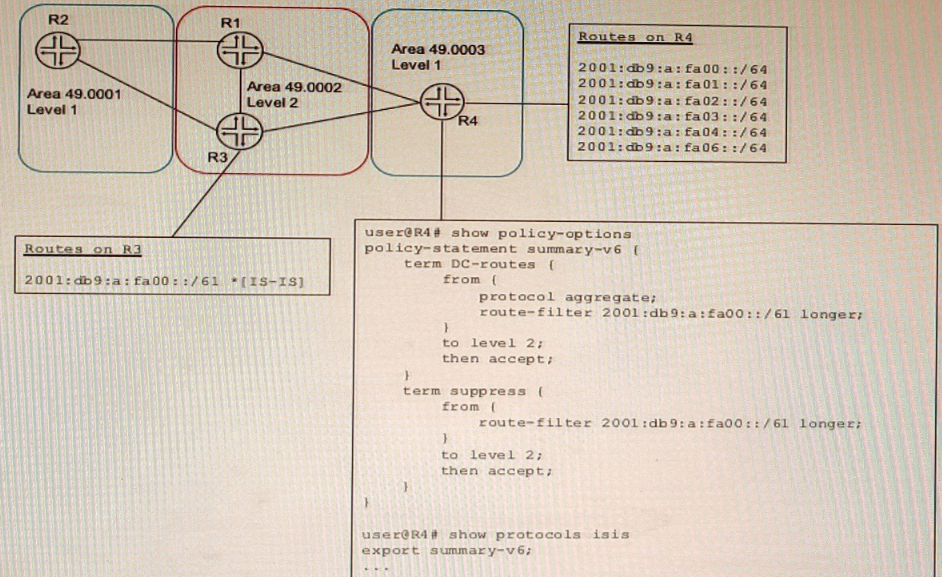
A network designer would like to create a summary route as shown in the exhibit, but the configuration is not working.
Which three configuration changes will create a summary route? (Choose three.)
To create a summary route for IS-IS, you need to configure a policy statement that matches the prefixes to be summarized and sets the next-hop to discard. You also need to configure a summary-address statement under the IS-IS protocol hierarchy that references the policy statement. In this case, the policy statement leak-v6 is trying to match the prefix 2001:db9:a:fa00::/61 exactly, but this prefix is not advertised by any router in the network. Therefore, no summary route is created. To fix this, you need to delete the longer keyword from the route-filter term and change the prefix length to /61 exact. This will match any prefix that falls within the /61 range. You also need to delete the export statement under protocols isis, because this will export all routes that match the policy statement to other IS-IS routers, which is not desired for a summary route.