At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Juniper JN0-636 exam questions by Juniper. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Juniper Security, Professional exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Juniper in their Juniper JN0-636 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Juniper Security, Professional exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Juniper JN0-636 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
You are required to deploy a security policy on an SRX Series device that blocks all known Tor network IP addresses. Which two steps will fulfill this requirement? (Choose two.)
The two steps that will fulfill the requirement of deploying a security policy on an SRX Series device that blocks all known Tor network IP addresses are enrolling the devices with Juniper ATP Cloud and enabling a third-party Tor feed. Juniper ATP Cloud is a cloud-based service that provides advanced threat detection and mitigation capabilities for SRX Series devices. By enrolling the devices with Juniper ATP Cloud, the devices can leverage the cloud intelligence and analytics to identify and block malicious traffic, including Tor traffic. A third-party Tor feed is a source of information that provides a list of IP addresses that are associated with the Tor network. By enabling a third-party Tor feed on the SRX Series device, the device can use the feed to create a dynamic address object that contains all the known Tor IP addresses. The device can then apply a security policy that denies traffic from or to the dynamic address object, effectively blocking the Tor network IP addresses.Reference: Juniper Security, Professional (JNCIP-SEC) Reference Materials source and documents: https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos/topics/concept/security-atp-cloud-overview.html https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos/topics/task/configuration/security-intelligence-third-party-feed-configuring.html
A company wants to paron their physical SRX series firewall into multiple logical units and assign
each unit (tenant) to a department within the organization. You are the primary administrator of firewall
and a colleague is the administrator for one of the departments.
Which two statements are correct about your colleague? (Choose two)
A)company wants to partition their physical SRX series firewall into multiple logical units and assign each unit (tenant) to a department within the organization. You are the primary administrator of the firewall and a colleague is the administrator for one of the departments. The two statements that are correct about your colleague are:
The other statements are incorrect because:
You want to configure a threat prevention policy.
Which three profiles are configurable in this scenario? (Choose three.)
The three profiles that are configurable in a threat prevention policy are infected host profile, C&C profile, and malware profile. A threat prevention policy is a feature of Juniper ATP Cloud that provides protection and monitoring for selected threat profiles, including command and control servers, infected hosts, and malware. Using feeds from Juniper ATP Cloud and optional custom feeds that you configure, ingress and egress traffic is monitored for suspicious content and behavior. Based on a threat score, detected threats are evaluated and action may be taken once a verdict is reached. You can create a threat prevention policy by selecting one or more of the following profiles:
Infected host profile: This profile detects and blocks traffic from hosts that are infected with malware or compromised by attackers. You can configure the threat score thresholds and the actions for different levels of severity. You can also enable Geo IP filtering to block traffic from or to specific countries or regions.
C&C profile: This profile detects and blocks traffic to or from command and control servers that are used by attackers to control malware or botnets. You can configure the threat score thresholds and the actions for different levels of severity. You can also enable Geo IP filtering to block traffic from or to specific countries or regions.
Malware profile: This profile detects and blocks traffic that contains malware or malicious content. You can configure the threat score thresholds and the actions for different levels of severity. You can also enable protocol-specific settings for HTTP and SMTP traffic, such as file type filtering, file size filtering, and file name filtering.
The other two profiles, device profile and SSL proxy profile, are not configurable in a threat prevention policy. A device profile is a feature of Policy Enforcer that defines the device type, the device group, and the device settings for the SRX Series devices that are enrolled with Juniper ATP Cloud. An SSL proxy profile is a feature of SRX Series devices that enables SSL proxy to decrypt and inspect SSL/TLS traffic for threats and policy violations.
Exhibit
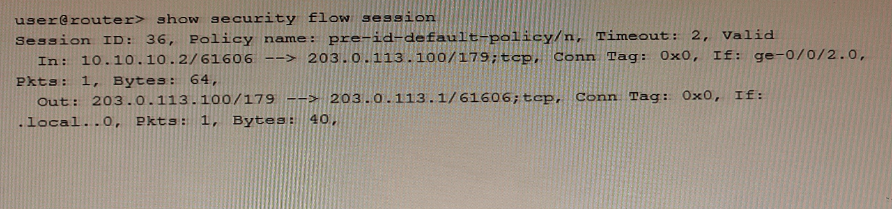
Referring to the exhibit, which type of NAT is being performed?
Source NAT is a type of NAT that is used to translate the source IP address and port number of a packet. This is typically used to allow multiple devices on a private network to access the internet using a single public IP address. In the exhibit, we can see that the source IP address and port number of the packet are being translated from 10.10.10.2/61606 to 203.0.113.100/179. This is a clear indication that Source NAT is being performed.Reference:
Network Address Translation Feature Guide
SRX NAT with Illustrated Examples
Exhibit:
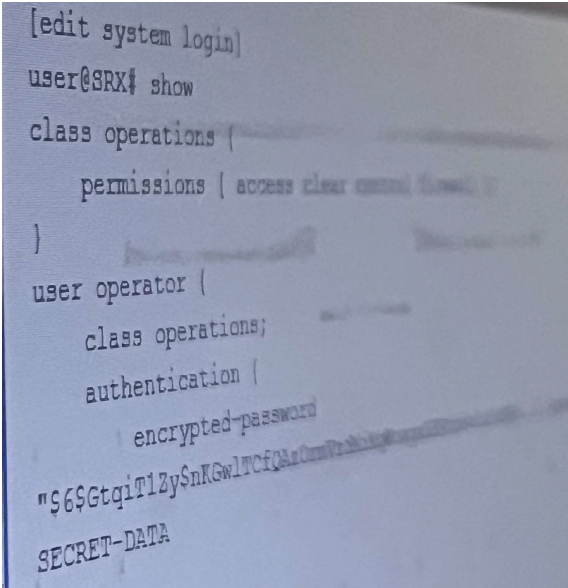
Referring to the exhibit, the operator user is unable to save configuration files to a usb stick the is
plugged into SRX. What should you do to solve this problem?
To solve the problem of the operator user being unable to save configuration files to a USB stick that is plugged into SRX, you need to add the system-control permission flag to the operations class. The other options are incorrect because:
Enter the configuration mode: user@host> configure
Navigate to the system login class hierarchy: user@host# edit system login class operations
Add the system-control permission flag: user@host# set permissions system-control
Commit the changes: user@host# commit
How to mount a USB drive on EX/SRX/MX/QFX Series platforms to import/export files