At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Huawei H31-161 exam questions by Huawei. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Huawei HCIE Carrier IP (Written) V1.0 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Huawei in their Huawei H31-161 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Huawei HCIE Carrier IP (Written) V1.0 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Huawei H31-161 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
If a (*, G) entry exists in the RP, which of the following statements about the source registration
process are true in PIM-SM?
Configure VRFs and relevant policies on a PE as follows:
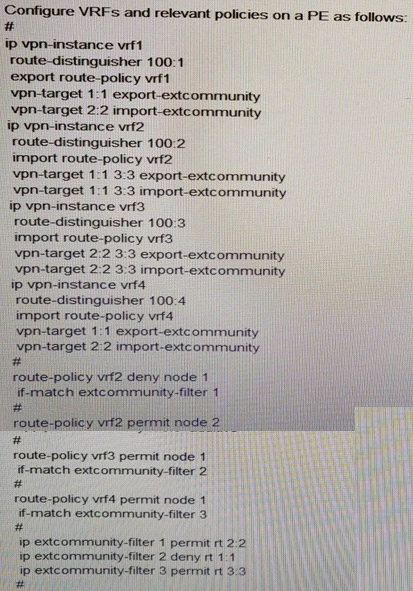
If a route is imported to the routing table of VRF 1, which VRF can the route match?
1. On the backbone network , if a PE is connect to a CE, VPN instances need to b reconfigured on the PE, and interface on the PE for connecting to the CE must be bound to a VPN instance. After binding an interface to a VPN instance, you must configure the IP address of the interface between PEs, IS-IS configured for PE interworking. PLSA basic capabilities and MPLS LSP are configured for LSP establishment, and MP _IBGP is configured for VPN route exchange VPN routes exchange , LDAP is short for Label Distribution Protocol, and IBGP is short for interior Border gateway protocol.
2. A CE exchange route exchange routers with a PE over External Border gateway Protocol (EBGP.
Configure interior gateway protocol (IGP) on the IS-IS+MPLS backbone networking to achieve the interworking between PEs and IP routers.
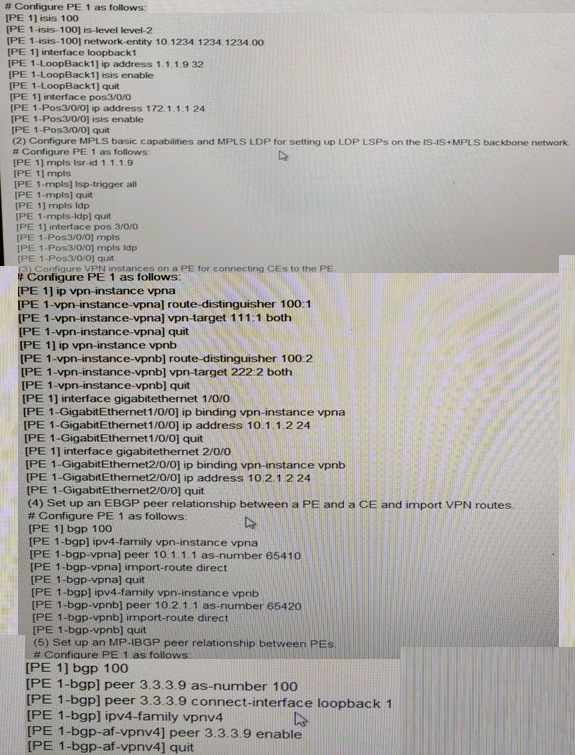
Refer to the exhibit.
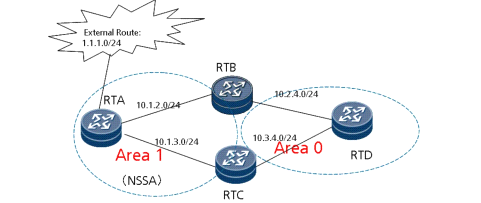
As shown in the figure, RT 5 is a stub area router, an external Internet route is imported by RT 1, and a virtual connection is established between RT 1 and RT 3.At present, the Internet is accessible to routers except RT 5. Why can the Internet not be accessed from RT 5?(Select two answers)