At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Huawei H12-351_V1.0 exam questions by Huawei. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Huawei HCIE-WLAN (Written) V1.0 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Huawei in their Huawei H12-351_V1.0 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Huawei HCIE-WLAN (Written) V1.0 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Huawei H12-351_V1.0 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
As shown in the figure, STA_1 through STA_4 are associated with AP_1, and STA_5 is associated with AP_2. Assuming that the load balancing threshold is 2, the load difference threshold is 25%, and API and AP2 support a maximum of 10 STAs, which of the following statements are true? (Select All that Apply)
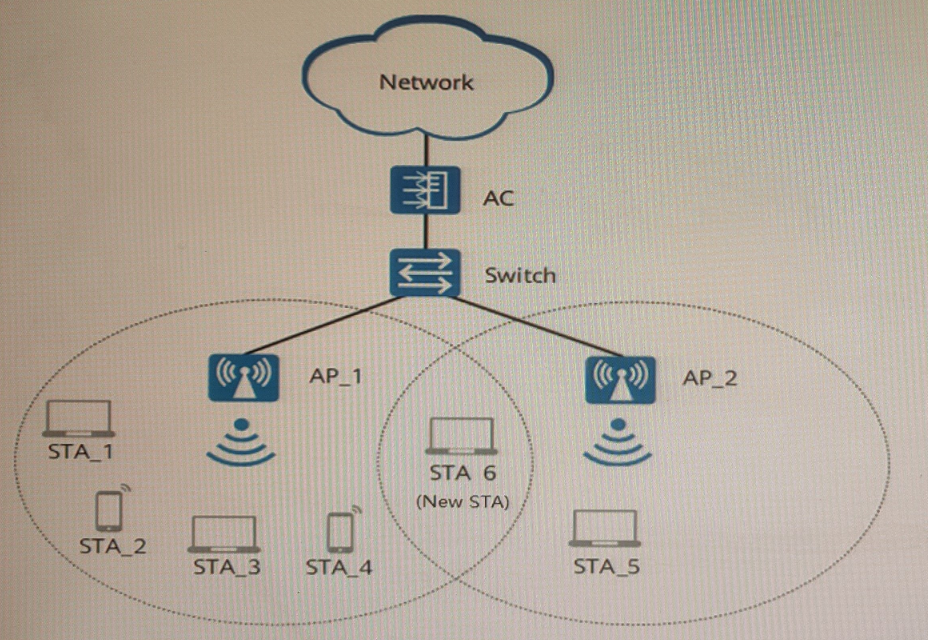
The load percentage of an AP is calculated by dividing the number of associated STAs by the maximum number of STAs supported by the AP. In this case, the load percentage of AP_1 is 4/10 = 40%, and that of AP_2 is 1/10 = 10%. The load balancing mechanism needs to be enabled to balance the load between AP_1 and AP_2. Then some STAs are steered from AP_1 to AP_2 based on the load balancing threshold and the load difference threshold.
Which of the following types of non-Wi-R devices can be identified by Huawei APs? (Select All that Apply)
Huawei APs can identify non-Wi-Fi devices that operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, such as Bluetooth devices, ZigBee devices, game controllers, wireless video and audio transmitters, microwave ovens, cordless phones, and baby monitors.
Which of the following statements about WLAN roaming and signal strength Is false?
B is false because generally, a STA roams when it detects that the signal strength is less than -70 dBm or -65 dBm, not -75 dBm.
Which of the following tools are commonly used for WLAN network planning, acceptance, or health evaluation? (Select All that Apply)
C is not a tool commonly used for WLAN network planning, acceptance, or health evaluation. eDesk is a tool for remote fault diagnosis and rectification on WLAN networks.
Which of the following components is not included In a typical RFID system?
A router is not included in a typical RFID system. A typical RFID system consists of three components: RFID tag, RFID reader, and information processing platform. The RFID tag is attached to the object to be identified, the RFID reader communicates with the tag and reads its information, and the information processing platform processes and stores the data collected by the reader.