At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the HPE7-A07 exam questions by HP. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Mobility Expert Written Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by HP in their HPE7-A07 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Mobility Expert Written Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the HPE7-A07 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
You configured a WPA3-SAE with the following MAC Authentication Role Mapping in Cloud Authentication and Policy:
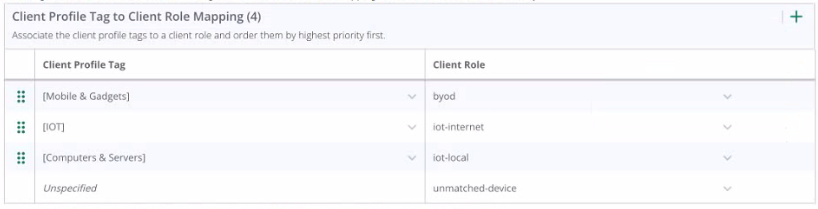
With further default settings assume a new Android phone is connected to the network. Which role will the client be assigned after connecting for the first time?
The configuration shown in the third exhibit details a client role mapping that associates different client profile tags with specific client roles. When a new device, such as an Android phone, connects to the network, it will be profiled and assigned a role based on the mappings defined. If the device does not match any predefined profiles, it would be assigned the 'unmatched-device' role. This is under the assumption that default settings are in place and the client does not match the criteria for any of the specific roles like 'byod', 'iot-internet', or 'iot-local'. Therefore, an Android phone connecting for the first time and not matching any specific profile tag would be assigned to the 'unmatched-device' role.
Which command would allow you to verity receipt of a CoA message on an AOS 10 GW?
The Change of Authorization (CoA) messages are used in network access control scenarios and are typically received by the network access server, in this case, an Aruba AOS 10 Gateway. The correct command to verify the receipt of a CoA message is related to the control path traffic because CoA is a control plane function.
Option B, packet-capture controlpath udp 3799, is the correct answer because it specifies capturing control plane traffic on UDP port 3799, which is the standard port for CoA messages.
Options A, C, and D are incorrect because:
Option A captures data plane traffic, not control plane traffic.
Option C's packet-capture interprocess udp 3799 does not refer to a standard command for capturing CoA messages.
Option D, tcpdump host-port 3799, does not specify the correct syntax for capturing traffic on Aruba devices.
You created a new SSID with the security settings shown in the exhibit.
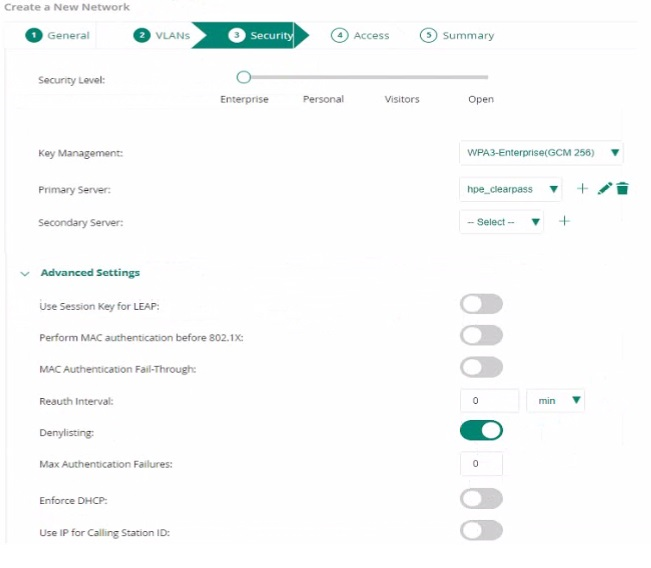
Some, but not all users complain that client devices are unable to connect to this SS1D. What is the reason for this?
If some users are unable to connect to an SSID configured with WPA3-Enterprise GCM-256, and the 'MAC Authentication Fall-Through' is disabled, it means that devices which fail 802.1X authentication will not attempt MAC authentication. If these client devices are configured to use MAC authentication as a backup method, they will fail to connect, explaining the issue faced by some users.
A customer has interfering devices that are seen over the air. They contact you and ask you to configure RAPIDS to help identify interfering and rogue APs. HPE Aruba Networking Central identifies a rogue AP and displays the connected switch port.
How can HPE Aruba Networking Central identify which switch port the AP is connected to?
HPE Aruba Networking Central can identify which switch port a rogue AP is connected to by using the switch's MAC address table. The MAC address table contains the associations between MAC addresses and the switch ports to which devices (including APs) are connected. When Aruba Central detects a rogue AP, it can look up the MAC address of the rogue AP in the switch's MAC address table to find the specific switch port it is connected to. This enables network administrators to quickly locate and address the rogue AP issue.
You configured a tunneled SSID with captive portal and a ClearPass Guest Self Registration workflow when testing and launching the self-registration workflow, after successful registration, the login action shows the following error:
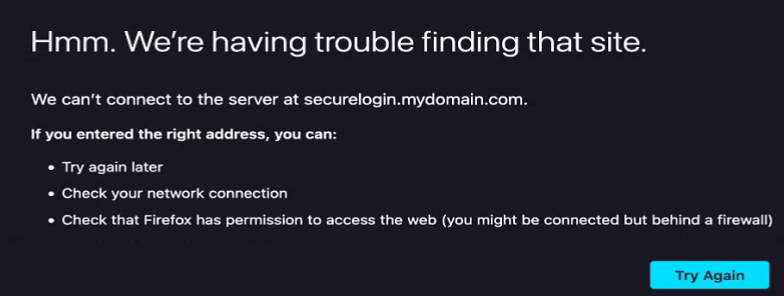
What is the best solution to resolve this error?
Including the root and intermediate certificates in the captive portal certificate for the gateway will resolve the error seen during the login action after successful registration. This is necessary to ensure the SSL/TLS handshake can be completed successfully, as the client browser needs to validate the entire certificate chain.