At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the HPE7-A01 exam questions by HP. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Professional Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by HP in their HPE7-A01 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Professional Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the HPE7-A01 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
A customer has a large number of food-producing machines
* All machines are connected via Aruba CX6200 switches in VLANs 100.110. and 120
* Several external technicians are maintaining this special equipment
What are the correct commands to ensure that no rogue DHCP server will impact the network?
A)

B)
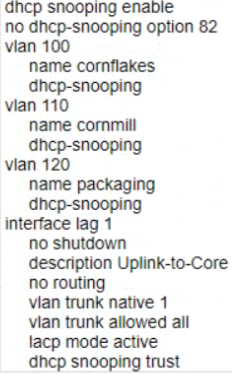
C)

D)

configures DHCP snooping on the switch and enables it for VLANs 100, 110, and 120. It also specifies the IP address of the authorized DHCP server and sets the ports connected to the server as trusted. This prevents any unauthorized DHCP server from providing invalid configuration data to the clients on those VLANs. Option B also enables DHCP option-82, which adds information about the switch port and VLAN to the DHCP packets, allowing for more granular control and logging of DHCP transactions.
A customer wants to deploy a Gateway and take advantage of all the SD-WAN features. Which persona role option should be selected?
The persona role option that should be selected to deploy a Gateway and take advantage of all the SD-WAN features is A. ArubaOS 10 Branch.
The other options are incorrect because:
D) ArubaOS 10 Mobility: This is a persona that enables the Gateway to act as a mobility controller for campus networks. It does not provide SD-WAN features.
Your Director of Security asks you to assign AOS-CX switch management roles to new employees based on their specific job requirements After the configuration was complete, it was noted that a user assigned with the administrators role did not have the appropriate level of access on the switch.
The user was not limited to viewing nonsensitive configuration information and a level of 1 was not assigned to their role Which default management role should have been assigned for the user?
The default management role that should have been assigned for the user is B. operators.