At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the HPE6-A84 exam questions by HP. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the HP Aruba Certified Network Security Expert Written Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by HP in their HPE6-A84 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their HP Aruba Certified Network Security Expert Written Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the HPE6-A84 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
What is a common characteristic of a beacon between a compromised device and a command and control server?
A beacon is a type of network traffic that is sent from a compromised device to a command and control (C2) server, which is a remote system that controls the malicious activities of the device . A beacon is used to establish and maintain communication between the device and the C2 server, as well as to receive instructions or exfiltrate data .
A common characteristic of a beacon is that it is periodic, meaning that it is sent at regular intervals, such as every few minutes or hours . This helps the C2 server to monitor the status and availability of the device, as well as to avoid detection by network security tools .
Another common characteristic of a beacon is that it is small and identically sized, meaning that it contains minimal or fixed amount of data, such as a simple acknowledgment or a random string . This helps the device to conserve bandwidth and resources, as well as to avoid detection by network security tools .
Refer to the scenario.
A customer is migrating from on-prem AD to Azure AD as its sole domain solution. The customer also manages both wired and wireless devices with Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune).
The customer wants to improve security for the network edge. You are helping the customer design a ClearPass deployment for this purpose. Aruba network devices will authenticate wireless and wired clients to an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) cluster (which uses version 6.10).
The customer has several requirements for authentication. The clients should only pass EAP-TLS authentication if a query to Azure AD shows that they have accounts in Azure AD. To further refine the clients' privileges, ClearPass also should use information collected by Intune to make access control decisions.
Assume that the Azure AD deployment has the proper prerequisites established.
You are planning the CPPM authentication source that you will reference as the authentication source in 802.1X services.
How should you set up this authentication source?
An authentication source is a configuration element in CPPM that defines how to connect to an external identity provider and retrieve user or device information . CPPM supports various types of authentication sources, such as Active Directory, LDAP, SQL, Kerberos, and HTTP .
To authenticate wireless and wired clients to Azure AD, you need to set up an authentication source as HTTP type, referencing Azure AD's FQDN . This type of authentication source allows CPPM to use REST API calls to communicate with Azure AD and validate the user or device credentials . You also need to configure the OAuth 2.0 settings for the authentication source, such as the client ID, client secret, token URL, and resource URL .
To use information collected by Intune to make access control decisions, you need to set up another authentication source as HTTP type, referencing the Intune extension . This type of authentication source allows CPPM to use REST API calls to communicate with Intune and retrieve the device compliance status . You also need to configure the OAuth 2.0 settings for the authentication source, such as the client ID, client secret, token URL, and resource URL .
Refer to the scenario.
A customer is using an AOS 10 architecture with Aruba APs and Aruba gateways (two per site). Admins have implemented auto-site clustering for gateways with the default gateway mode disabled. WLANs use tunneled mode to the gateways.
The WLAN security is WPA3-Enterprise with authentication to an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) cluster VIP. RADIUS communications use RADIUS, not RadSec.
CPPM is using the service shown in the exhibits.
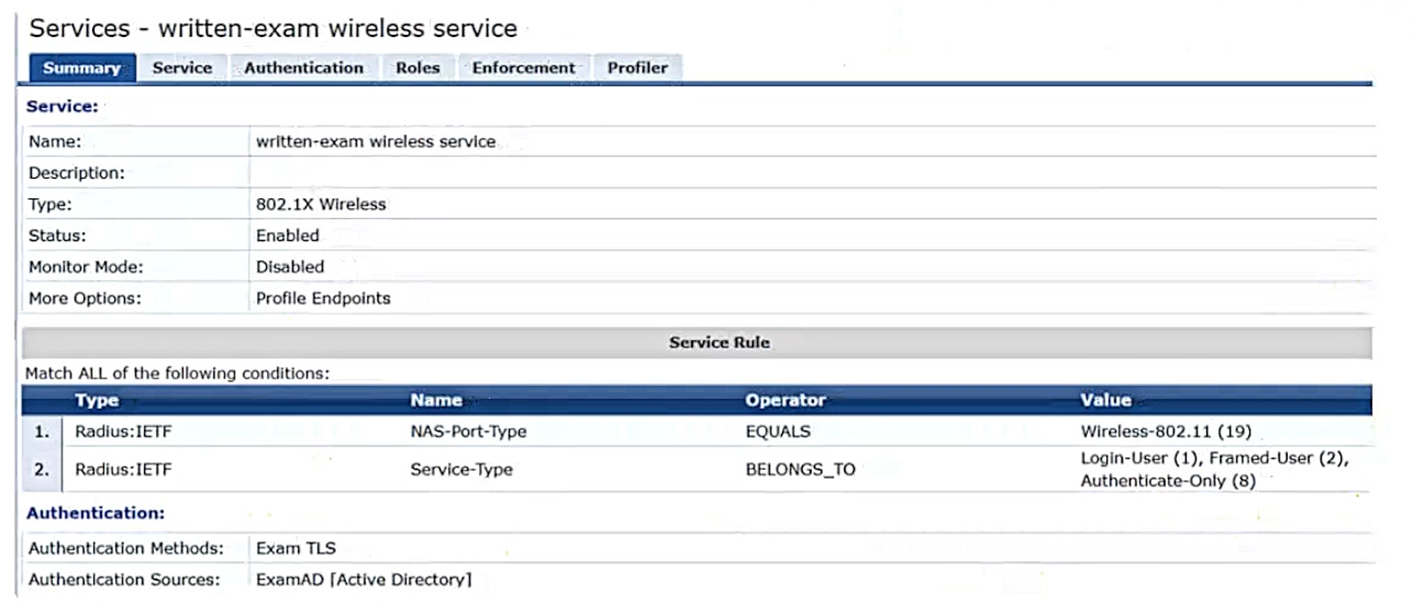
Which step can you take to improve operations during a possible gateway failover event?
Auto-site clustering is a feature that allows gateways in the same site and group to form a cluster automatically. However, this mode does not support VRRP IP addresses, which are required for dynamic authorization (CoA) from ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) to the gateways. Dynamic authorization is a mechanism that allows CPPM to change the attributes or status of a client session on the gateways without requiring re-authentication. This is useful for applying policies, roles, or bandwidth limits based on various conditions. Without VRRP IP addresses, CPPM would not be able to send CoA messages to the correct gateway in case of a failover event, resulting in inconsistent or incorrect client behavior.
To enable VRRP IP addresses for dynamic authorization, you need to set up gateway clusters manually and assign a VRRP VLAN and a VRRP IP address to each cluster. This way, CPPM can use the VRRP IP address as the NAS IP address for RADIUS communications and CoA messages. The VRRP IP address will remain the same even if the active gateway in the cluster changes due to a failover event, ensuring seamless operations. You can find more information about how to set up gateway clusters manually and configure VRRP IP addresses in the Gateway Cluster Deployment - Aruba page and the ClearPass Policy Manager User Guide1.
You are working with a developer to design a custom NAE script for a customer. The NAE agent should trigger an alert when ARP inspection drops packets on a VLAN. The customer wants the admins to be able to select the correct VLAN ID for the agent to monitor when they create the agent.
What should you tell the developer to do?
A custom NAE script is a Python script that defines the monitors, the alert-trigger logic, and the remedial actions for an NAE agent. A monitor is a URI that specifies the data source and the data type that the NAE agent should collect and analyze. For example, to monitor the ARP inspection statistics on a VLAN, the monitor URI would be something like this:

where <vlan-id> is the ID of the VLAN to be monitored.
To allow the admins to select the correct VLAN ID for the agent to monitor when they create the agent, you need to define a VLAN ID parameter in the NAE script. A parameter is a variable that can be set by the user when creating or modifying an agent. A parameter can be referenced in other parts of the script by using the syntax ${parameter-name}. For example, to define a VLAN ID parameter and reference it in the monitor URI, you would write something like this:

This way, when the admins create or modify the agent, they can enter the VLAN ID that they want to monitor, and the NAE script will use that value in the monitor URI.
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows C