At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE8_812 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 8 - Written Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE8_812 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 8 - Written Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE8_812 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Refer to the exhibit.
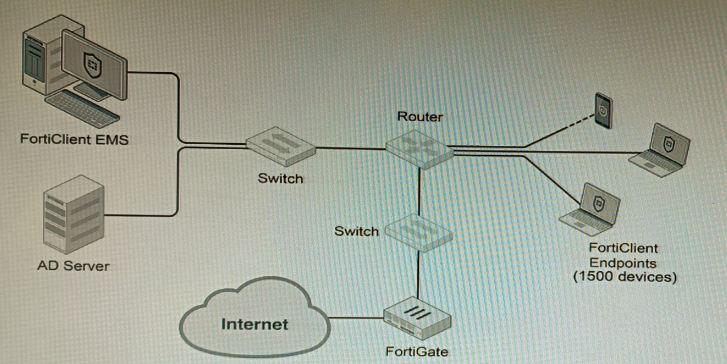
A customer wants FortiClient EMS configured to deploy to 1500 endpoints. The deployment will be integrated with FortiOS and there is an Active Directory server.
Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, which two statements about the installation are correct? (Choose two.)
Ais correct because if no client update time is specified on EMS, the user will be able to choose the time of installation if they wish to delay. This is because the FortiClient EMS server will not force the installation on the client.
Eis correct because the Windows clients only require 'File and Printer Sharing' allowed and the rest is handled by Active Directory group policy. This is because the Active Directory group policy will configure the Windows clients to automatically install FortiClient and the FortiClient EMS server will only need to push the initial configuration to the clients.
The other options are incorrect. Option B is incorrect because a client can only be eligible for one enabled configuration on the EMS server. Option C is incorrect because you can deploy initial installations to both Windows and macOS clients. Option D is incorrect because you can use the included SQL Server Express to deploy FortiClient EMS.
Deploying FortiClient EMS | FortiClient / FortiOS 7.4.0 - Fortinet Document Library
Configuring FortiClient EMS | FortiClient / FortiOS 7.4.0 - Fortinet Document Library
FortiClient EMS installation requirements | FortiClient / FortiOS 7.4.0 - Fortinet Document Library
Refer to the exhibit.
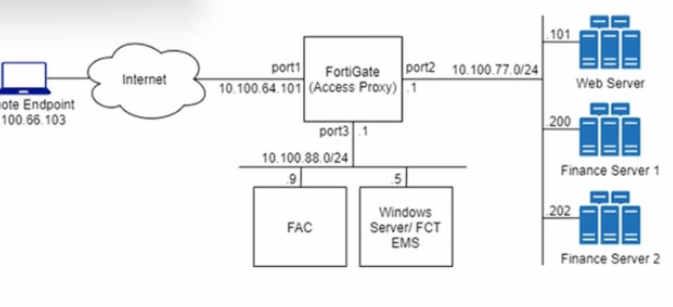
An HTTPS access proxy is configured to demonstrate its function as a reverse proxy on behalf of the web server it is protecting. It verifies user identity, device identity, and trust context, before granting access to the protected source. It is assumed that the FortiGate EMS fabric connector has already been successfully connected.
You need to ensure that ZTNA access through the FortiGate will redirect users to the FortiAuthenticator to perform username/password and multifactor authentication to validate access prior to accessing resources behind the FortiGate.
In this scenario, which two further steps need to be taken on the FortiGate? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit.
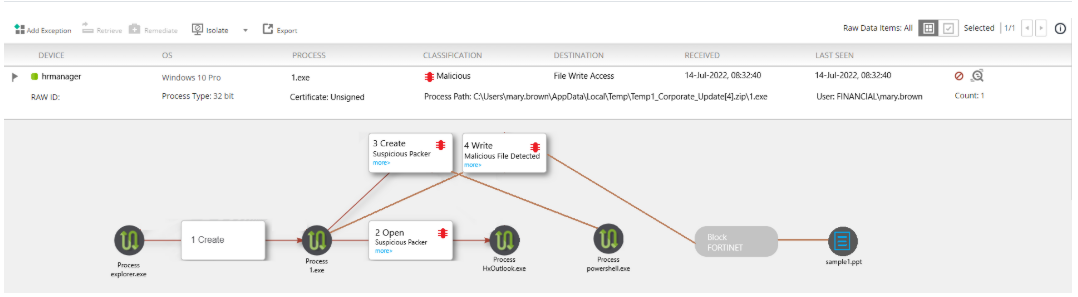
The exhibit shows the forensics analysis of an event detected by the FortiEDR core
In this scenario, which statement is correct regarding the threat?
A customer is planning on moving their secondary data center to a cloud-based laaS. They want to place all the Oracle-based systems Oracle Cloud, while the other systems will be on Microsoft Azure with ExpressRoute service to their main data center.
They have about 200 branches with two internet services as their only WAN connections. As a security consultant you are asked to design an architecture using Fortinet products with security, redundancy and performance as a priority.
Which two design options are true based on these requirements? (Choose two.)
A . Systems running on Azure will need to go through the main data center to access the services on Oracle Cloud. This is because the Oracle Cloud is not directly connected to the Azure Cloud. The traffic will need to go through the main data center in order to reach the Oracle Cloud.
C . Branch FortiGate devices must be configured as VPN clients for the branches' internal network to be able to access Oracle services without using public IPs. This is because the Oracle Cloud does not allow direct connections from the internet. The traffic will need to go through the FortiGate devices in order to reach the Oracle Cloud.
The other options are not correct.
B . Use FortiGate VM for IPSEC over ExpressRoute, as traffic is not encrypted by Azure. This is not necessary. Azure does encrypt traffic over ExpressRoute.
D . Two ExpressRoute services to the main data center are required to implement SD-WAN between a FortiGate VM in Azure and a FortiGate device at the data center edge. This is not necessary. A single ExpressRoute service can be used to implement SD-WAN between a FortiGate VM in Azure and a FortiGate device at the data center edge.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/expressroute/expressroute-about-encryption
Refer to the exhibit.
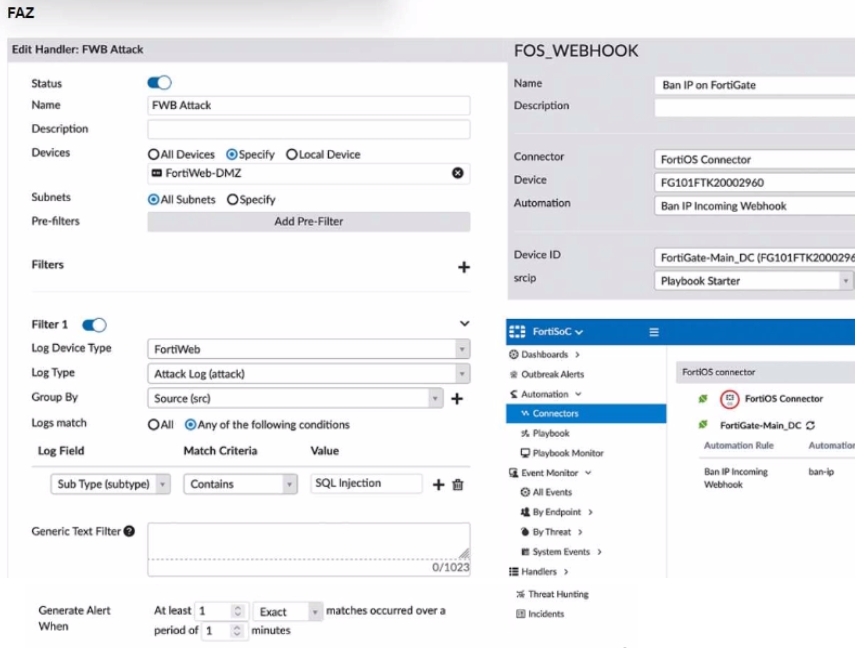
A customer is trying to setup a Playbook automation using a FortiAnalyzer, FortiWeb and FortiGate. The intention is to have the FortiGate quarantine any source of SQL Injection detected by the FortiWeb. They got the automation stitch to trigger on the FortiGate when simulating an attack to their website, but the quarantine object was created with the IP 0.0.0.0. Referring to the configuration and logs in the exhibits, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)