At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE7_ZTA-7.2 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 7 - Zero Trust Access 7.2 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE7_ZTA-7.2 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 7 - Zero Trust Access 7.2 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE7_ZTA-7.2 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Which statement is true regarding a FortiClient quarantine using FortiAnalyzer playbooks?
FortiAnalyzer playbooks are automated workflows that can perform actions based on triggers, conditions, and outputs. One of the actions that a playbook can perform is to quarantine a device by sending an API call to FortiClient EMS, which then instructs the FortiClient agent on the device to disconnect from the network. This can help isolate and contain a compromised or non-compliant device from spreading malware or violating policies.Reference:=
Quarantine a device from FortiAnalyzer playbooks
Exhibit.
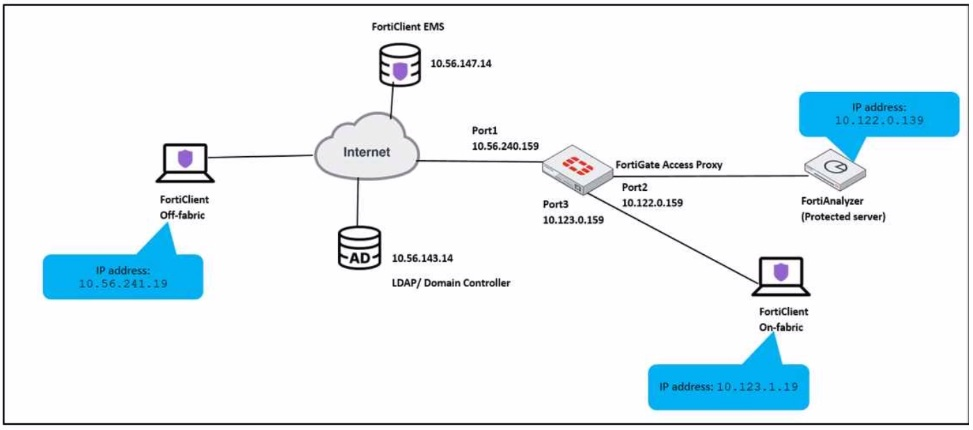
An administrator has to provide on-fabric clients with access to FortiAnalyzer using ZTNA tags
Which two conditions must be met to achieve this task? (Choose two.)
For on-fabric clients to access FortiAnalyzer using ZTNA tags, the following conditions must be met:
A) The on-fabric client should have FortiGate as its default gateway: This is essential to ensure that all client traffic is routed through FortiGate, where ZTNA policies can be enforced.
B) The ZTNA server must be configured on FortiGate: For ZTNA tags to be effectively used, the ZTNA server, which processes and enforces these tags, must be configured on the FortiGate appliance.
Configuring ZTNA tags and tagging rules
Synchronizing FortiClient ZTNA tags
Technical Tip: ZTNA Tags fail to synchronize between FortiClient and FortiGate
Which factor is a prerequisite on FortiNAC to add a Layer 3 router to its inventory?
In which FortiNAC configuration stage do you define endpoint compliance?
Which three core products are mandatory in the Fortinet ZTNA solution'' {Choose three.)
Fortinet ZTNA solution is a zero-trust network access approach that provides secure and granular access to applications hosted anywhere, for users working from anywhere. The three core products that are mandatory in the Fortinet ZTNA solution are:
FortiClient EMS: This is the central management console that orchestrates the ZTNA policies and provides visibility and control over the endpoints and devices. It also integrates with FortiAuthenticator for identity verification and FortiAnalyzer for reporting and analytics.
FortiClient: This is the endpoint agent that supports ZTNA, VPN, endpoint protection, and vulnerability scanning. It establishes encrypted tunnels with the ZTNA proxy on the FortiGate and provides device posture and single sign-on (SSO) capabilities.
FortiGate: This is the next-generation firewall that acts as the ZTNA proxy and enforces the ZTNA policies based on user identity, device posture, and application context. It also provides security inspection and threat prevention for the ZTNA traffic.