At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE7_PBC-6.4 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 7 - Public Cloud Security 6.4 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE7_PBC-6.4 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 7 - Public Cloud Security 6.4 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE7_PBC-6.4 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
You have been asked to develop an Azure Resource Manager infrastructure as a code template for the FortiGate-VM, that can be reused for multiple deployments. The deployment fails, and errors point to the storageAccount name.
Which two are restrictions for a storageAccount name in an Azure Resource Manager template? (Choose two.)
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/templates/microsoft.storage/storageaccounts?tabs=bicep
Property values / storageAccounts
name --> The resource name :
* string (required)
* Character limit: 3-24
* Valid characters: Lowercase letters and numbers.
* Resource name must be unique across Azure.
Which two statements about Microsoft Azure network security groups are true? (Choose two.)
An organization deploys a FortiGate-VM (VM04 / c4.xlarge) in Amazon Web Services (AWS) and configures two elastic network interfaces (ENIs). Now, the same organization wants to add additional ENIs to support different workloads in their environment.
Which action can you take to accomplish this?
Refer to the exhibit.
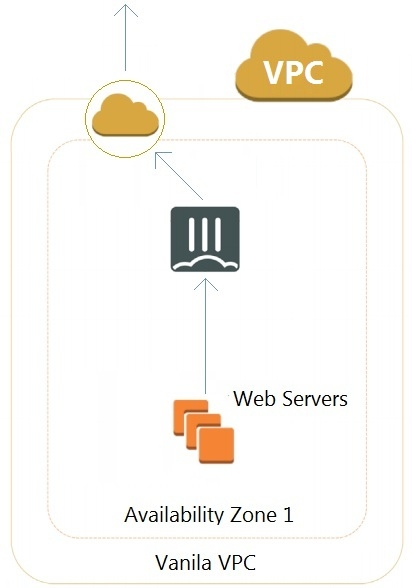
A customer has deployed an environment in Amazon Web Services (AWS) and is now trying to send outbound traffic from the Web servers to the Internet. The FortiGate policies are configured to allow all outbound traffic; however, the traffic is not reaching the FortiGate internal interface.
What are two possible reasons for this behavior? (Choose two.)
You need to check if source/destination are enabled. Public_Cloud_6.4_Study_Guide Page 67
An organization deployed a FortiGate-VM in the Google Cloud Platform and initially configured it with two vNICs. Now, the same organization wants to add additional vNICs to this existing FortiGate-VM to support different workloads in their environment.
How can they do this?