At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE6_FAC-6.4 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiAuthenticator 6.4 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE6_FAC-6.4 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiAuthenticator 6.4 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE6_FAC-6.4 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
You are the administrator of a global enterprise with three FortiAuthenticator devices. You would like to deploy them to provide active-passive HA at headquarters, with geographically distributed load balancing.
What would the role settings be?
To deploy three FortiAuthenticator devices to provide active-passive HA at headquarters, with geographically distributed load balancing, the role settings would be:
One standalone primary, which acts as the master device for HA and load balancing
One cluster member, which acts as the backup device for HA and load balancing
One load balancer, which acts as a remote device that forwards authentication requests to the primary or cluster member device
Which FSSO discovery method transparently detects logged off users without having to rely on external features such as WMI polling?
FortiClient SSO Mobility Agent is a FSSO discovery method that transparently detects logged off users without having to rely on external features such as WMI polling. FortiClient SSO Mobility Agent is a software agent that runs on Windows devices and communicates with FortiAuthenticator to provide FSSO information. The agent can detect user logon and logoff events without using WMI polling, which can reduce network traffic and improve performance.
At a minimum, which two configurations are required to enable guest portal services on FortiAuthenticator? (Choose two)
To enable guest portal services on FortiAuthenticator, you need to configure a portal policy that defines the conditions for presenting the guest portal to users and the authentication methods to use. You also need to configure at least one post-login service that defines what actions to take after a user logs in successfully, such as sending an email confirmation, assigning a VLAN, or creating a user account. Configuring a RADIUS client or an external authentication portal are optional steps that depend on your network setup and requirements. Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4/administration-guide/372404/guest-management
Which of the following is an OATH-based standard to generate event-based, one-time password tokens?
HOTP stands for HMAC-based One-time Password, which is an OATH-based standard to generate event-based OTP tokens. HOTP uses a cryptographic hash function called HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) to generate OTPs based on two pieces of information: a secret key and a counter. The counter is incremented by one after each OTP generation, creating an event-based sequence of OTPs.
Examine the screenshot shown in the exhibit.
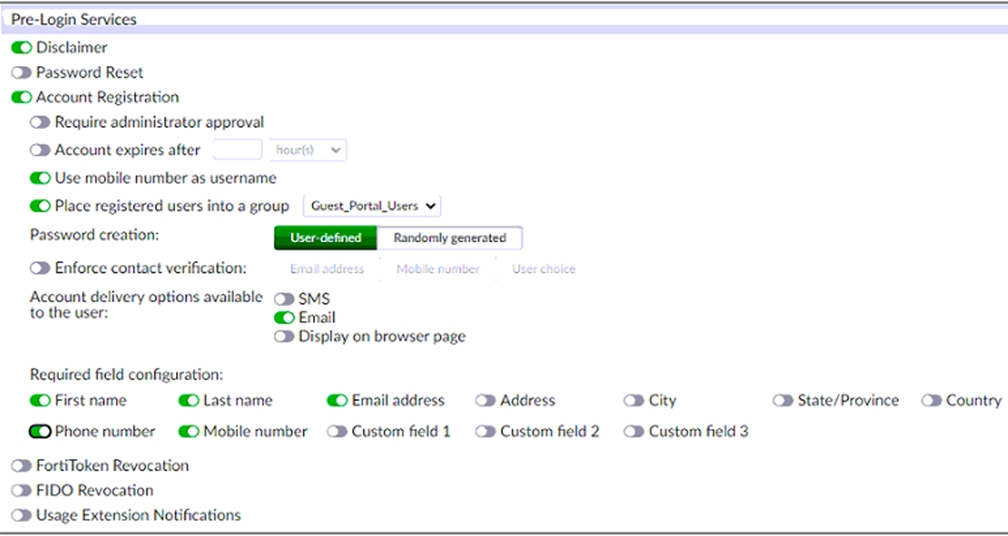
Which two statements regarding the configuration are true? (Choose two.)
The screenshot shows that the account registration feature is enabled for the guest portal and that the guest group is set to Guest_Portal_Users.This means that all guest accounts created using this feature will be placed under that group1. The screenshot also shows that email validation is enabled for the guest portal and that the email validation link expires after 24 hours.This means that all accounts registered through the guest portal must be validated through email within that time frame1.