At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet NSE5_FSM-6.3 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet NSE 5 - FortiSIEM 6.3 exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet NSE5_FSM-6.3 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet NSE 5 - FortiSIEM 6.3 exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet NSE5_FSM-6.3 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Which discovery scan type is prone to miss a device, if the device is quiet and the entry foe that device is not present in the ARP table of adjacent devices?
Discovery Scan Types: FortiSIEM uses various scan types to discover devices on a network.
Layer 2 (L2) Scan: An L2 scan discovers devices based on ARP tables and MAC address information from adjacent devices.
Limitation: If a device is quiet (not actively communicating) and its entry is not present in the ARP table of adjacent devices, the L2 scan may miss it.
Other Scan Types:
CMDB Scan: Based on the existing Configuration Management Database (CMDB) entries.
Range Scan: Scans a specified IP range for devices.
Smart Scan: Uses a combination of methods to discover devices.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Device Discovery section, which explains the different types of discovery scans and their characteristics.
FortiSIEM is deployed in disaster recovery mode.
When disaster strikes, which two tasks must you perform manually to achieve a successful disaster recovery operation? (Choose two.)
Disaster Recovery Mode: FortiSIEM's disaster recovery (DR) mode ensures that there is a backup system ready to take over in case the primary system fails.
Manual Tasks for DR Operation: In the event of a disaster, certain tasks must be performed manually to ensure a smooth transition to the secondary system.
Promoting the Secondary Supervisor:
Use the command phSecondary2primary to promote the secondary supervisor to the primary role. This command reconfigures the secondary supervisor to take over as the primary supervisor, ensuring continuity in management and coordination.
Changing DNS Configuration:
Update the DNS configuration to direct all users, devices, and collectors to the secondary FortiSIEM instance. This ensures that all components in the environment can communicate with the newly promoted primary supervisor without manual reconfiguration of individual devices.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 Administration Guide, Disaster Recovery section, provides detailed steps on promoting the secondary supervisor and updating DNS configurations during a disaster recovery operation.
Refer to the exhibit.
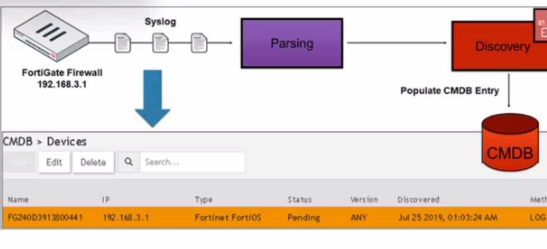
How was the FortiGate device discovered by FortiSIEM?
Discovery Methods in FortiSIEM: FortiSIEM can discover devices using various methods, including syslog, SNMP, and others.
Syslog Discovery: The exhibit shows that the FortiGate device is discovered by FortiSIEM using syslog.
Syslog Parsing: The syslog messages sent by the FortiGate device are parsed by FortiSIEM to extract relevant information.
CMDB Entry: Based on the parsed information, an entry is populated in the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) for the device.
Evidence in Exhibit: The exhibit shows the syslog flow from the FortiGate Firewall to the parsing and discovery process, resulting in the device being listed in the CMDB with the status 'Pending.'
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Device Discovery section, which explains how syslog discovery works and how devices are added to the CMDB based on syslog data.
Refer to the exhibit.
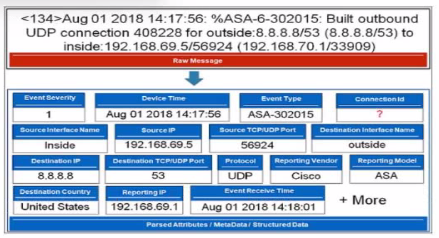
Which value will FortiSIEM use to populate the Connection Id field?
When configuring collectors located in geographically separated sites, what ports must be open on a front end firewall?
FortiSIEM Architecture: In FortiSIEM, collectors gather data from various sources and send this data to supervisors and workers within the FortiSIEM architecture.
Communication Requirements: For collectors to effectively send data to the FortiSIEM system, specific communication channels must be open.
Port Usage: The primary port used for secure communication between the collectors and the FortiSIEM infrastructure is HTTPS (port 443).
Network Configuration: When configuring collectors in geographically separated sites, the HTTPS port must be open for the collectors to communicate with both the supervisor and the worker upload settings addresses. This ensures that the collected data can be securely transmitted to the appropriate processing and analysis components.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 Administration Guide, Network Ports section details the necessary ports for communication within the FortiSIEM architecture.