At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
What does the command set forward-domain
In a transparent mode Virtual Domain (VDOM) configuration, FortiGate operates as a Layer 2 bridge rather than performing Layer 3 routing. The set forward-domain <domain_ID> command is used to control how traffic is forwarded between interfaces within the same transparent VDOM.
A forward-domain acts as a broadcast domain, meaning only interfaces with the same forward-domain ID can exchange traffic. This setting is commonly used to separate different VLANs or network segments within the transparent VDOM while still allowing FortiGate to apply security policies.
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a partial VPN configuration.

What can you conclude from this VPN IPsec phase 1 configuration?
This IPsec Phase 1 configuration defines a dynamic VPN tunnel that can accept connections from multiple peers. The settings chosen here suggest a configuration optimized for networks with intermittent traffic patterns while ensuring resources are used efficiently.
Key configurations and their impact:
set type dynamic This allows multiple peers to establish connections dynamically without needing predefined IP addresses.
set ike-version 2 Uses IKEv2, which is more efficient and supports features like EAP authentication and reduced rekeying overhead.
set dpd on-idle Dead Peer Detection (DPD) is triggered only when the tunnel is idle, reducing unnecessary keep-alive packets and improving resource utilization.
set add-route enable FortiGate automatically adds the route to the routing table when the tunnel is established, ensuring connectivity when needed.
set proposal aes128-sha256 aes256-sha256 Uses strong encryption and hashing algorithms, ensuring a secure connection.
set keylife 28800 Sets a longer key lifetime (8 hours), reducing the frequency of rekeying, which is beneficial for stable connections.
Because DPD is set to on-idle, the tunnel will not constantly send keep-alive messages but will still ensure connectivity when traffic is detected. This makes the configuration ideal for networks with regular but non-continuous traffic, balancing security and resource efficiency.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a command output.

FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B are members of an FGSP cluster in an enterprise network.
While testing the cluster using the ping command, the administrator monitors packet loss and found that the session output on FortiGate_B is as shown in the exhibit.
What could be the cause of this output on FortiGate_B?
The Fortinet FGSP (FortiGate Session Life Support Protocol) cluster allows session synchronization between two FortiGate devices to provide seamless failover. However, ICMP (ping) is a connectionless protocol, and by default, FortiGate does not synchronize connectionless sessions unless explicitly enabled.
In the exhibit:
The command get system session list | grep icmp on FortiGate_B returns no output, meaning that ICMP sessions are not being synchronized from FortiGate_A.
If session-pickup-connectionless is disabled, FortiGate_B will not receive ICMP sessions, causing packet loss during failover.
An administrator needs to install an IPS profile without triggering false positives that can impact applications and cause problems with the user's normal traffic flow.
Which action can the administrator take to prevent false positives on IPS analysis?
False positives in Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) analysis can disrupt legitimate traffic and negatively impact user experience. To reduce false positives while maintaining security, administrators can:
Use IPS profile extensions to fine-tune the settings based on the organization's environment.
Select the correct operating system, protocol, and application types to ensure that IPS signatures match the network's actual traffic patterns, reducing false positives.
Customize signature selection based on the network's specific services, filtering out unnecessary or irrelevant signatures.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the ADVPN IPsec interface representing the VPN IPsec phase 1 from Hub A to Spoke 1 and Spoke 2, and from Hub to Spoke 3 and Spoke 4.
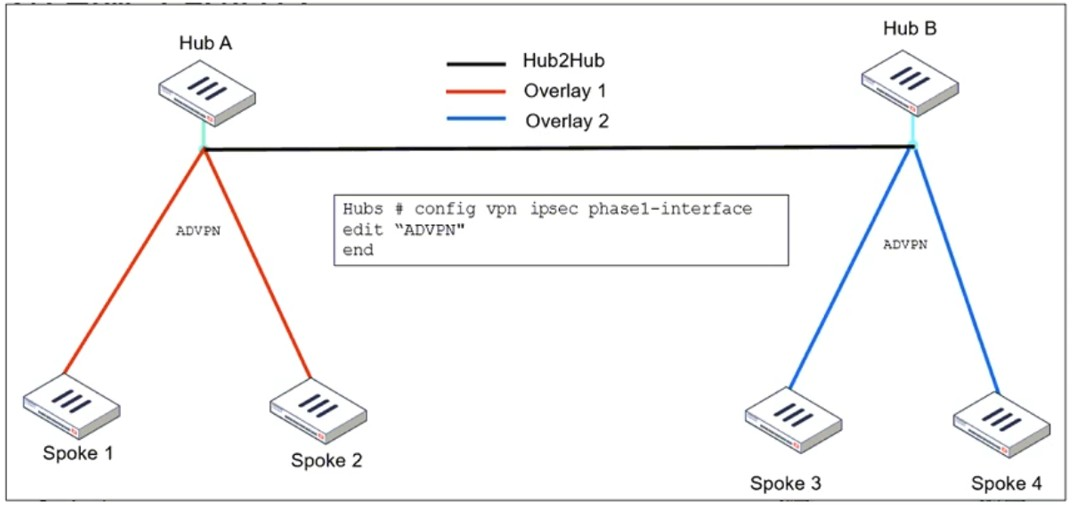
An administrator must configure an ADVPN using IBGP and EBGP to connect overlay network 1 with 2.
What must the administrator configure in the phase 1 VPN IPsec configuration of the ADVPN tunnels?
When configuring ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) to connect overlay networks across different hubs using IBGP and EBGP, special configurations are required to allow spokes from different overlay networks to dynamically establish tunnels.
set auto-discovery-crossover enable
This allows cross-hub tunnel discovery in an ADVPN deployment where multiple hubs are used.
Since Hub A and Hub B belong to different overlays, enabling crossover discovery ensures that spokes from one overlay can dynamically create direct tunnels to spokes in the other overlay when needed.
set enforce-multihop enable
This setting ensures that BGP peers using loopback interfaces can establish connectivity even if they are not directly connected.
Multihop BGP sessions are required when using loopback addresses as BGP peer sources because the connection might need to traverse multiple routers before reaching the BGP neighbor.
This is especially useful in ADVPN deployments with multiple hubs, where routes might need to cross from one hub to another.