At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Fortinet FCP_WCS_AD-7.4 exam questions by Fortinet. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Fortinet FCP - AWS Cloud Security 7.4 Administrator exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Fortinet in their Fortinet FCP_WCS_AD-7.4 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Fortinet FCP - AWS Cloud Security 7.4 Administrator exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Fortinet FCP_WCS_AD-7.4 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
Refer to the exhibit.
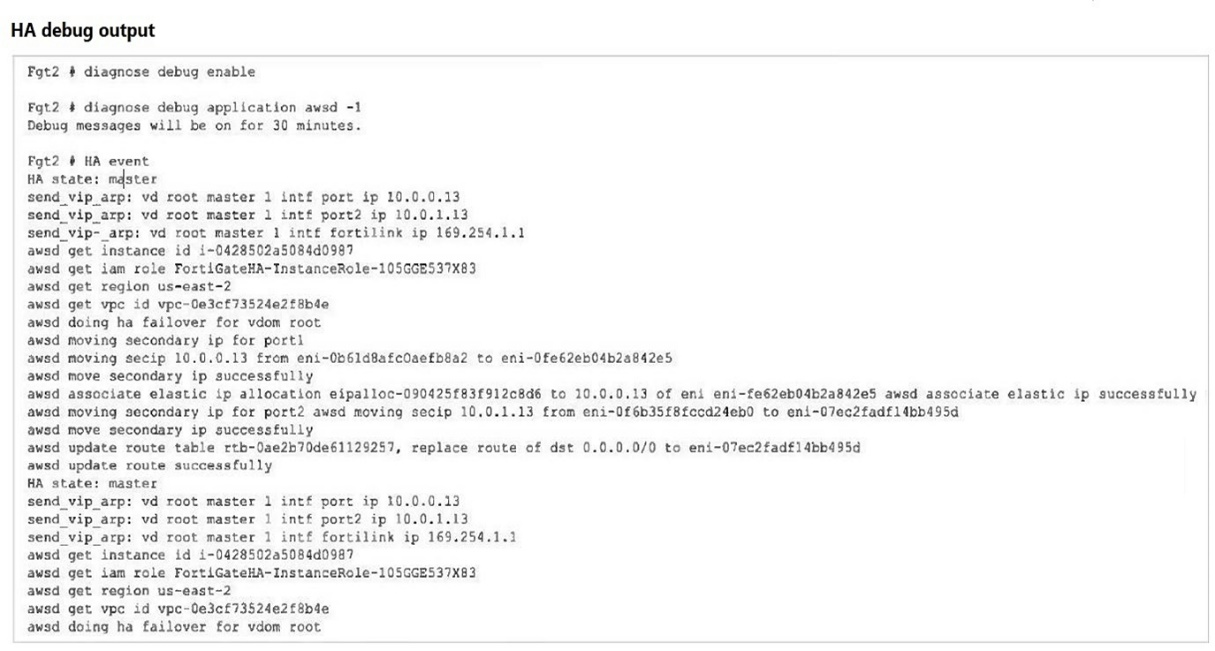
You deployed an active-passive FortiGate HA cluster using a CloudFormation template on an existing VPC. Now you want to test active-passive FortiGate HA failover by running a debug so you can see the API calls to change the Elastic and secondary IP addresses.
Which statement is correct about the output of the debug?
HA Event and Failover:
The debug output indicates that a failover event occurred and the secondary instance (Fgt2) is now taking over as the master.
Elastic IP Association:
The debug output shows the process of moving the Elastic IP (eipalloc-090425f83f912c8d6) to the new master instance. This involves associating the Elastic IP with the appropriate network interface (eni) of the new master.
Specific IP Address Association:
The Elastic IP is specifically associated with port1 of Fgt2. The message 'associate elastic ip eipalloc-090425f83f912c8d6 to 10.0.0.13 of eni eni-0f6b35f8fccd24eb0' indicates that the Elastic IP is now linked to the primary IP address (10.0.0.13) on port1 of the new master.
Other Options Analysis:
Option A is incorrect because the routing table update details are not explicitly stated.
Option C is incorrect because the IP address association mentioned relates to an Elastic IP, not eni-0b61d8afc0aefb8a2.
Option D is incorrect because it specifically mentions port2 for the Elastic IP association, which is not indicated in the debug output.
FortiGate HA Configuration Guide: FortiGate HA
A customer is attempting to deploy an active-passive high availability (HA) cluster using the software-defined network (SDN) connector in the AWS cloud.
What is an important consideration to ensure a successful formation of HA, failover, and traffic flow?
HA Cluster in AWS Cloud:
Deploying an active-passive HA cluster in AWS requires careful consideration of the clustering protocol used to ensure seamless failover and traffic flow.
Unicast FortiGate Clustering Protocol (FGCP):
Unicast FGCP is specifically designed for environments where multicast traffic is not feasible or supported, such as in the AWS cloud. Using unicast FGCP ensures that heartbeat and synchronization traffic between the cluster members are managed correctly over unicast communication, which is suitable for AWS's network infrastructure (Option C).
Comparison with Other Options:
Option A is incorrect because while placing both cluster members in the same availability zone might be required for certain configurations, it is not the critical factor for HA formation.
Option B is incorrect as VDOM exceptions are not directly related to the successful formation of HA.
Option D is incorrect because the ELB configuration checks are more about ensuring that the load balancer correctly routes traffic but do not specifically ensure HA formation and failover.
FortiGate HA in AWS Documentation: FortiGate HA
Fortinet FGCP Details: FGCP Documentation
You need to deploy a new Windows server in AWS to offload web traffic from an existing web server in a different availability zone.
According to the AWS shared responsibility model, what three actions must you take to secure the new EC2 instance? (Choose three.)
Update Software:
As part of the AWS shared responsibility model, it is the customer's responsibility to update and maintain the software running on the EC2 instance, including applying security patches and updates (Option A).
Configure Security Groups:
Security groups act as virtual firewalls for instances to control inbound and outbound traffic. Configuring them correctly is essential for securing the EC2 instance and ensuring only legitimate traffic can reach the server (Option C).
Manage Operating System:
Managing the operating system, including user accounts, permissions, and operating system patches, is the responsibility of the customer under the shared responsibility model (Option D).
Other Options Analysis:
Option B is incorrect as changing the existing ELB to a gateway load balancer is not necessary for securing the new EC2 instance.
Option E is incorrect because it is not required to move all web servers into the same availability zone for security purposes.
A global organization with cloud networks deployed in several AWS regions wants to set up next-generation firewall (NGFW) protection using FortiGate Cloud-Native Firewall (CNF).
What are two deployment considerations for the organization? (Choose two.)
Regional Deployment:
For a global organization with cloud networks in multiple AWS regions, a separate FortiGate Cloud-Native Firewall (CNF) instance is required for each AWS region to provide localized protection and meet compliance requirements. This ensures that each region has its own dedicated NGFW protection tailored to its specific needs (Option B).
Multi-Account Association:
FortiGate CNF supports associating multiple AWS accounts with a single CNF instance. This feature is beneficial for organizations that operate in a multi-account setup, allowing centralized management and security policies across different accounts (Option C).
Other Options Analysis:
Option A is incorrect because AWS Firewall Manager is a different service and is not required to provision a CNF instance.
Option D is incorrect because a single CNF instance cannot protect multiple AWS regions due to regional isolation in AWS.
FortiGate CNF Documentation: FortiGate CNF
Your organization is deciding between deploying FortiWeb VM or Fortinet Managed Rules for AWS WAF.
What are two benefits of choosing FortiWeb VM? (Choose two.)
Zero-day Protection:
FortiWeb VM provides robust protection against zero-day vulnerabilities through advanced security mechanisms and frequent updates from FortiGuard. This ensures that web applications are protected from newly discovered threats that have not yet been patched or recognized by other security systems (Option C).
Advanced WAF Functionality:
FortiWeb VM offers a range of advanced WAF features that go beyond what is typically provided by managed rules for AWS WAF. These include more detailed traffic analysis, customizable rules, machine learning-based threat detection, and comprehensive logging and reporting capabilities (Option D).
Other Options Analysis:
Option A is more relevant to a consumption-based pricing model but not a specific benefit unique to FortiWeb VM over AWS WAF.
Option B is incorrect because both FortiWeb VM and Fortinet Managed Rules for AWS WAF are powered by FortiGuard updates.
FortiWeb Overview: FortiWeb VM