At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Arcitura Education C90.06 exam questions by Arcitura Education. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Arcitura Education Cloud Architecture Lab exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Arcitura Education in their Arcitura Education C90.06 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Arcitura Education Cloud Architecture Lab exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Arcitura Education C90.06 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
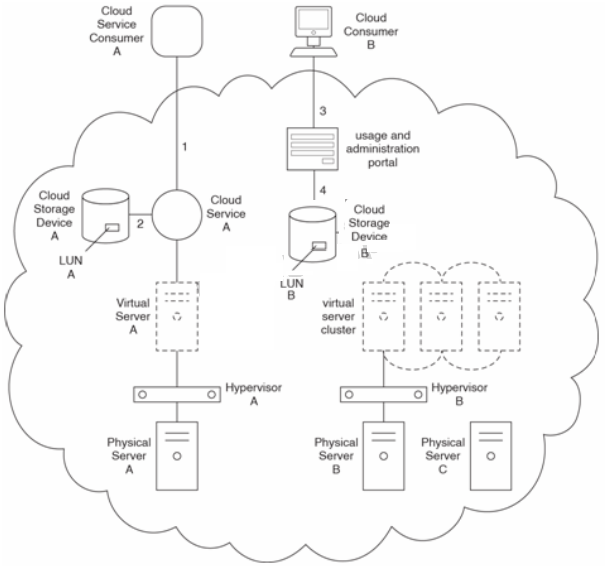
Cloud Service A and Cloud Service B perform different functions but both share access to Cloud Storage Device A when fulfilling requests from cloud service consumers that require data access.
Cloud Services A and B are hosted by Virtual Server A, which is hosted by Hypervisor A on Physical Server A.
Cloud Service Consumer A accesses Cloud Service A to issue a request for data (1). Cloud Service A queries a database in Cloud Storage Device A to retrieve the data (2). Upon receiving the requested data, Cloud Service Consumer A combines it with additional data to form a new collection of data. Cloud Service Consumer A then accesses Cloud Service B and provides it with the new data (3). Cloud Service B accesses a different database in Cloud Storage Device A to store the new data (4). Cloud Consumer B accesses the usage and administration portal to upload new data (5). The data is uploaded to Cloud Storage Device B (6).
Cloud Service Consumer A belongs to Organization A. Cloud Consumer B belongs to Organization B.
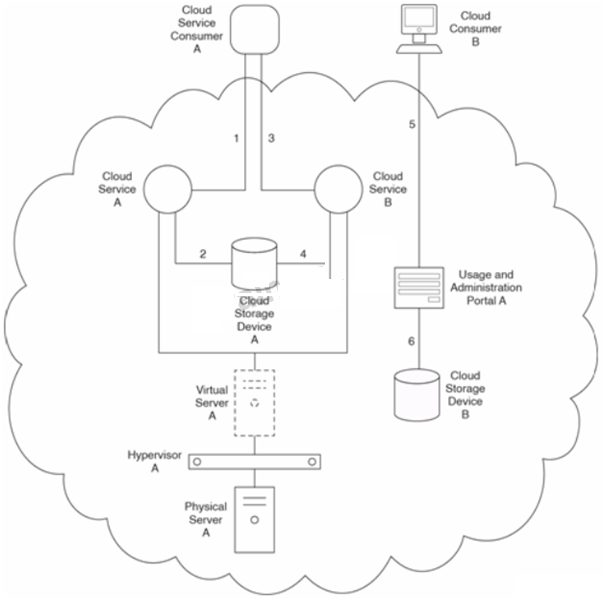
Cloud Service A is a SaaS product offered by the cloud provider to the general public, and is therefore used by numerous cloud consumers from different organizations at different times. Cloud Service B is also a SaaS product as part of the same overall solution as Cloud Service A.
However, because a given cloud service consumer only needs to access Cloud Service B when the data it receives from Cloud Service A meets certain criteria, it is not used nearly as much as Cloud Service A. Cloud Service A currently has a hard threshold allowing no more than 10 concurrent instances of it to exist at once. One day, Cloud Service Consumer A attempts to access Cloud Service A as the eleventh cloud service consumer, and is predictably rejected.
Cloud Service Consumer A belongs to Organization A, one of the cloud provider's most important customers. Therefore, when Organization A complains about not being able to access Cloud Service A during peak usage times, the cloud provider agrees to provide a solution.
As a result of a natural disaster, the cloud provider's data center that houses Physical Server A becomes unexpectedly unavailable. Physical Server A subsequently becomes unavailable for nearly two days. This outage exceeds what the cloud provider guaranteed in its original SLA and the cloud provider agrees to not charge Organization for usage fees for an entire month as compensation. However, the unavailability of Physical Server A had a significant impact on Organization As business, resulting in financial loss and loss of confidence of its clients.
Organization A informs the cloud provider that it cannot continue working with this cloud unless the cloud provider can guarantee that the availability of Physical Server A will no longer be dependent on a single data center or a single geographic region.
Organization B receives its latest monthly invoice from the cloud provider and discovers that the charges are identical to the invoice it received last month, even though the usage and administration portal shows that its data usage is a third less. They bring this issue to the attention of the cloud provider and are informed that they are currently subscribed to a fixed-allocation plan.
The cloud provider explains that in order to get them on a plan whereby they are charged only for actual data usage, Cloud Storage Device B would need to be upgraded and a system capable of tracking runtime usage would need to be established. Organization B asks the cloud provider to make these changes.
Which of the following statements provides a solution that can address Organization A's and Organization B's issues?
Cloud Service A requires access to Cloud Storage Device A, which contains LUNs A and B. Cloud Service A is hosted by Virtual Server A, which resides on Hypervisor A on Physical Server A.
Virtual Server B hosts Cloud Service B and Cloud Service C.
Cloud Service Consumer A accesses Cloud Service A (1), which then accesses LUN A or B on Cloud Storage Device A (2). After receiving the requested data from Cloud Service A, Cloud Service Consumer A forwards the data to Cloud Service B (3), which then writes it to Cloud Storage Device B (4).
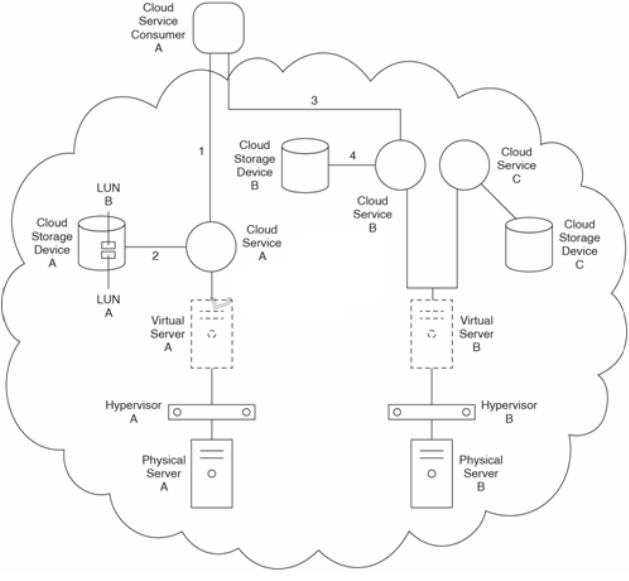
Cloud Service Consumer A belongs to Organization A,
Organization A uses LUN A and LUN B on Cloud Storage Device A to store their important client account data. Cloud Storage Device A is a low-performance cloud storage device, which begins to cause performance issues as more data is added to LUNs A and B and as Cloud Service Consumer A performs data access requests more frequently. Organization A asks that its cloud architecture be upgraded to process increased quantities of data and higher volumes of data requests.
Organization A has been leasing a PaaS environment that it used to build Cloud Service A, which it would like to make available to the general public. Organization A needs to establish a system capable of monitoring usage of Cloud Service A for billing purposes.
The cloud provider is using a usage data collection and reporting system that gathers information on Organization A's hosted IT resources approximately ten hours after the time of usage. One day, Organization A attempts to retrieve information on whether Virtual Server B has available Cloud Service C instances. They discover that they are unable to obtain the current status of Virtual Server B. Organization A demands a system that provides instant availability reporting.
Which of the following statements lists the patterns that can be applied to solve these three requirements and problems?
Ready-Made Environment A is hosted by Virtual Server A and Ready-Made Environments is hosted by Virtual Server B. Virtual Servers A and B are hosted by Hypervisor A, which is part of a hypervisor cluster. An automated scaling listener intercepts cloud consumer requests and automatically invokes the on-demand generation of additional instances of ready-made environments, as required.
A self-service portal and a usage and administration portal are also available to cloud consumers.
The self-service portal can be used to request the provisioning of a new ready-made environment.
Any cloud consumer that has already had a ready-made environment provisioned can configure and view information about that ready-made environment via the usage and administration portal.
Cloud Consumer A accesses Ready-Made Environment A to work on the development of a new cloud service (1). Cloud Consumer B accesses Ready-Made Environment B to test a recently completed application comprised of three cloud services (2). Cloud Consumer C accesses the self-service portal to request the creation of a new ready-made environment (3).
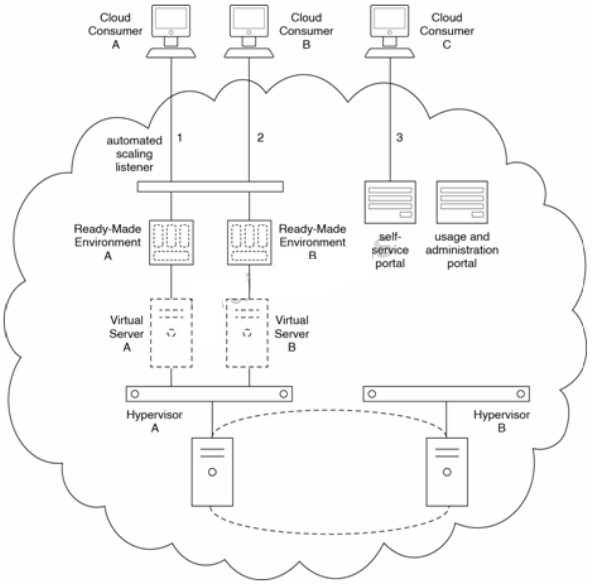
The cloud provider is required to perform an emergency maintenance outage on a cloud storage device used by all ready-made environments. The unplanned outage takes two hours. During this period, Cloud Consumers A and B are unable to access Ready-Made Environments A and B and Cloud Consumer C receives an error when submitting a request to create a new ready-made environment.
After the maintenance outage is over, Cloud Consumers A and B encounter the following problems:
Cloud Consumer A is unable to recover session data that was kept in memory for an extended period, prior to the time of the outage.
Cloud Consumer B has no access to Virtual Server B, which was moved to Hypervisor B during the maintenance outage. When Cloud Consumer B attempts to ping Virtual Server B, the request times out.
Even though Cloud Consumer C is able to log into the usage and administration portal to confirm that its ready-made environment was successfully provisioned, the unexpected outage has raised concerns about the stability of the ready-made environment's underlying infrastructure. Cloud Consumer C informs the cloud provider that it cannot proceed with its lease of the ready-made environment if there are future occurrences of this type of maintenance outage.
Which of the following statements can help address the problems and concerns of the three cloud consumers?
Cloud Service A accesses LUN Aon Cloud Storage Device A when it receives requests to process data from cloud consumers. Cloud Service A is hosted by Virtual Server A. The usage and administration portal can be used to access and manage the data in Cloud Storage Device B, which is also hosted by Virtual Server A. Virtual Server A is further hosted by Hypervisor A, which resides on Physical Server A. Virtual Server B is part of a virtual server cluster hosted by Hypervisor B. which resides on Physical Server B. Physical Server C is not in use and does not yet have an operating system installed.
Cloud Service Consumer A sends a request to Cloud Service A (1), which accesses data in LUN Aon Cloud Storage Device A (2). Cloud Consumer B uses the usage and administration portal to upload new data (3). The data is placed in LUN B on Cloud Storage Device B (4).
Cloud Service Consumer A and Cloud Consumer B belong to Organization A, which is leasing Virtual Server A and Virtual Server B from the cloud provider. Organization A also proceeds to lease Physical Server C as part of a new laaS agreement it signs with the cloud provider.
Organization A wants to provision Physical Server C with a number of legacy systems that cannot be deployed on virtual servers. However, when it attempts to do so, it realizes that its laaS package only provides Physical Server C as an out-of-the-box hardware server without anything installed on it. In order to deploy its legacy systems Organization A requires that Physical Server C first has an operating system installed, but it has no means of remotely provisioning Physical Server C with an operating system.
Organization A would like to deploy two of its legacy systems on Virtual Server A and to further extend Cloud Service A's functions so that it can be used as an external interface for cloud service consumers to access legacy system features. Additionally, Organization A would like to deploy three of its mission-critical legacy systems on Virtual Server B in order to take advantage of the additional performance and failover benefits provided by the virtual server cluster that Virtual Server B is part of. Each of the five legacy systems is comprised of dozens of components that need to be installed individually. Instead of manually installing each component of each legacy system, Organization A would like to customize workflows that can automate these deployment tasks.
During the first few months of working with its cloud-based legacy systems. Organization A receives a number of complaints from users that the cloud-based legacy systems are at times behaving erratically. However, when cloud resource administrators with Organization A review the cloud provider's reports that log usage, downtime and other runtime characteristics, they do not find any indication of erratic behavior or any other comparable problems. After some further investigation, the cloud resource administrators determine that the nature of the erratic behavior is specific to proprietary features of the legacy systems and is therefore not monitored or logged by the cloud provider's standard audit monitor, pay-per-use monitor or automated scaling listener.
The cloud resource administrators recommend that a new service agent be developed with features customized to monitor the legacy systems.
Which of the following statements provides a solution that can address Organization A's requirements?
Cloud Service A is installed on Virtual Server A and the database it accesses is located on Cloud Storage Device A. Both Virtual Servers A and B are hosted by Hypervisor A. Requests from cloud
service consumers are intercepted by an automated scaling listener that automatically routes subsequent requests to additional instances of Cloud Service A whenever the given usage of an instance exceeds two concurrent requests.
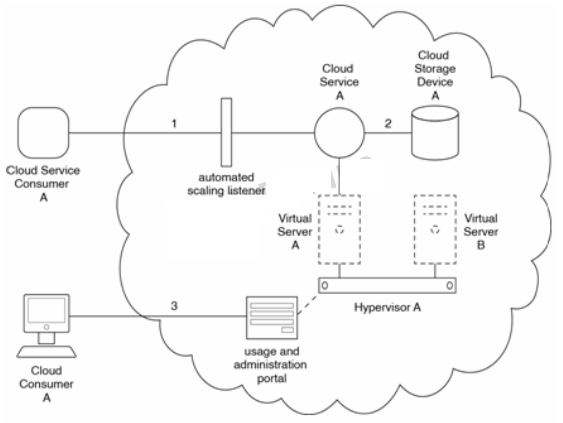
Cloud Service Consumer A accesses Cloud Service A (1), which either sends a query or a read/write request to a database on Cloud Storage Device A (2). A usage and administration portal is available, enabling Cloud Consumer A to view the billing and usage history of Virtual Servers A and B (3).
Cloud Service Consumer A and Cloud Consumer A are owned by Organization A. which performs several tests on the cloud architecture that produce the following results:
A stress test is performed to generate workloads on Virtual Servers A and B to gauge their load capacity. This test reveals that both virtual servers have firm workload thresholds. If the workload capacity on either virtual server reaches its threshold, further processing requests are rejected.
An availability test shows that Cloud Service A becomes unavailable whenever Hypervisor A crashes.
A security test is carried out during which the cloud architecture is accessed by a malicious cloud consumer that disables the path used by Cloud Service A to access Cloud Storage Device A, thereby causing all subsequent cloud service consumer requests to be replied to with data access errors.
Which of the following statements describes a solution that addresses the concerns raised by the three tests?