At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the Appian ACD101 exam questions by Appian. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the Appian Certified Associate Developer exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by Appian in their Appian ACD101 exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their Appian Certified Associate Developer exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the Appian ACD101 exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
After selecting a record, a user wants to initiate an activity in the context of that selected record.
You start by creating the process model that implements this activity.
What should you do next?
a record related action. This allows the action to be performed in the context of a specific record, making it straightforward for users to initiate processes directly from the record view. Reference:
Appian Documentation: Record Related Actions
You are creating a form used to order a pizz
a. You use a radio button component for the selection.
The pizza selection labels include a list of toppings. You do not want the selection labels to be truncated.
Which layout should you choose?
For a pizza ordering form where you do not want the radio button selection labels to be truncated, the Stacked layout is the most appropriate. This layout will list the options vertically, giving each one adequate space and preventing truncation, which is particularly useful when the labels include longer text, such as a list of toppings. Reference: Appian Documentation - Interface Components
You have a record type, ABC_Author, backed by a database table.
You need to retrieve the total number of authors without loading all the data.
According to Appian best practices, which code snippet accomplishes this goal in the most efficient way?
A)

B)
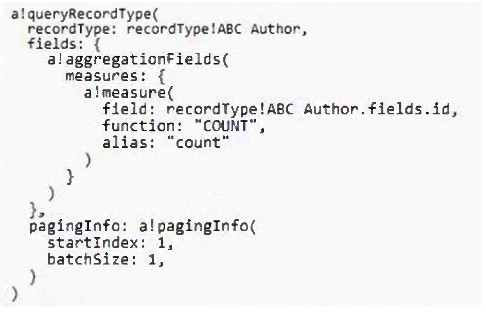
C)

According to Appian best practices, the most efficient way to retrieve the total number of authors without loading all the data is to use a query that includes an aggregation function. Option B uses an aggregation field with a COUNT function, which is designed to return the number of rows that match a query without the need to retrieve and load all row data, thus optimizing performance.
Appian Documentation: a!queryRecordType Function
You are configuring a Related Action for an entity-backed record type.
What is the proper domain prefix to reference the record data that will be passed into the Process Model as context for the Record Action?
When configuring a Related Action for an entity-backed record type, the proper domain prefix to reference the record data passed into the Process Model as context for the Record Action is pv!. This prefix stands for process variables, which are used to pass data into and out of a process model. In the context of a Related Action, pv! would be used to reference the specific process variables that are configured to receive the record data. Reference: Appian Documentation - Process Variables and Record Types
Which step can be critical in passing information from a form back to a process model?
The critical step in passing information from a form back to a process model is to configure inputs on the Data tab of a User Input Task. When you create a User Input Task, it includes a form for users to interact with. The data entered into this form can be mapped to process variables via the Data tab configuration. This ensures that the information collected in the form is available to the process for further use. Reference: Appian Documentation - User Input Tasks