At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the APA FPC-Remote exam questions by APA. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the APA Fundamental Payroll Certification Exam exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by APA in their APA FPC-Remote exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their APA Fundamental Payroll Certification Exam exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the APA FPC-Remote exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
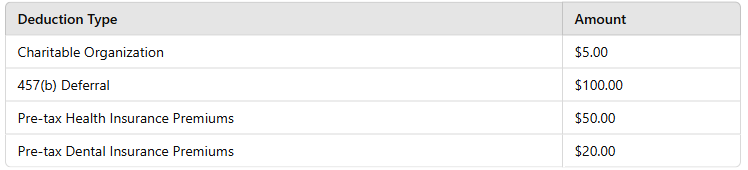
During open enrollment, the employee elects the following deductions. What is the total of the Section 125 Cafeteria Plan deductions?
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Section 125 Cafeteria Plan deductions include only pre-tax health and dental insurance contributions.
Eligible Pre-Tax Deductions:
Health Insurance Premiums: $50.00
Dental Insurance Premiums: $20.00
Total Section 125 Deductions: $70.00
Non-Eligible Deductions:
Charitable Contributions ($5.00) Not pre-tax.
457(b) Deferral ($100.00) Retirement savings, not a Section 125 deduction.
Thus, the correct answer is A. $70.00.
IRS -- Section 125 Cafeteria Plan Guidelines
Payroll.org -- Employee Benefit Deduction Compliance
Payroll standard operating procedures should be updated no less frequently than:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Payroll Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) must be regularly updated to maintain compliance and accuracy.
Best practice is to update SOPs whenever workflows change (Option C).
Option A (Annually) is incorrect because waiting a full year could lead to outdated procedures.
Option B (Quarterly) is incorrect unless payroll processes are highly dynamic.
Option D (When management changes) is incorrect because processes may change independently of leadership changes.
Payroll.org -- Payroll Policies and Procedures Best Practices
IRS -- Payroll Compliance Guidelines
Employers can take advantage of all of the following affordability safe harbors set forth in the ACA regulations EXCEPT:
ACA affordability safe harbors include (A), (C), and (D), but NOT Section 530 (B), which relates to independent contractor classification.
Affordable Care Act Compliance Guide
All of the following workflow mapping descriptions are correct EXCEPT:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Workflow mapping is a visual representation of payroll processes to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
Option A (Logical thought processes) ensures clarity and eliminates assumptions.
Option B (Depictions of sequences) accurately describes workflow design.
Option C (Steps follow without delay) ensures process efficiency.
Option D is incorrect because it describes Service Level Agreements (SLA), not workflow mapping.
Payroll.org -- Payroll Workflow Mapping Guide
Process Improvement Standards -- Payroll System Optimization
Documentation on legislative changes to Forms W-2 and W-3 is initiated by which of the following organizations?
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is responsible for issuing updates related to Forms W-2 and W-3 under federal tax laws.
SSA (Social Security Administration) processes W-2s but does not initiate changes.
OCSS (Office of Child Support Services) and USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) are not involved in payroll tax forms.
IRS Publication 15 (Employer's Tax Guide)
IRS Form W-2 & W-3 Guidelines