At ValidExamDumps, we consistently monitor updates to the AICPA CPA-Auditing exam questions by AICPA. Whenever our team identifies changes in the exam questions,exam objectives, exam focus areas or in exam requirements, We immediately update our exam questions for both PDF and online practice exams. This commitment ensures our customers always have access to the most current and accurate questions. By preparing with these actual questions, our customers can successfully pass the AICPA CPA Auditing and Attestation exam on their first attempt without needing additional materials or study guides.
Other certification materials providers often include outdated or removed questions by AICPA in their AICPA CPA-Auditing exam. These outdated questions lead to customers failing their AICPA CPA Auditing and Attestation exam. In contrast, we ensure our questions bank includes only precise and up-to-date questions, guaranteeing their presence in your actual exam. Our main priority is your success in the AICPA CPA-Auditing exam, not profiting from selling obsolete exam questions in PDF or Online Practice Test.
May an accountant accept an engagement to compile or review the financial statements of a not-for-profit entity if the accountant is unfamiliar with the specialized industry accounting principles, but plans to obtain the required level of knowledge before compiling or reviewing the financial statements?

Choice 'd' is correct. Knowledge of the accounting principles and practices of the industry is required in order to perform a compilation or review engagement; however, there is no requirement that such knowledge be obtained prior to accepting such an engagement.
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'c' are incorrect, per above.
An auditor compared the current-year gross margin with the prior-year gross margin to determine if cost of sales is reasonable. What type of audit procedure was performed?
Choice 'b' is correct. Analytical procedures are evaluations of financial information made by a study of plausible relationships among data, and they include comparisons between current year and prior year financial information.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Tests of transactions involve selecting specific transactions and evaluating whether they were properly recorded. Comparing current year and prior year gross margin would not provide information regarding specific transactions.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. Tests of controls are performed to evaluate the effectiveness of controls.
Comparing current year and prior year gross margin would not provide information regarding controls.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. Test of details are audit procedures used to gather evidence to support specific account balances. Comparing current year and prior year gross margin does not provide much information regarding specific account balances, although it might identify an account balance worthy of further consideration.
In evaluating the reasonableness of an accounting estimate, an auditor most likely would concentrate on key factors and assumptions that are:
Choice 'd' is correct. In evaluating the reasonableness of an estimate, an auditor would normally concentrate on key factors and assumptions that are (1) significant to the accounting estimate, (2) sensitive to variations, (3) deviations from historical patterns, or (4) subjective and susceptible to misstatements and bias.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. The auditor need not concentrate on key factors or assumptions that are consistent with those of prior periods, since estimates based on such assumptions are less likely to be misstated.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. The auditor need not concentrate on key factors or assumptions that are similar to industry guidelines, since estimates based on such assumptions are less likely to be misstated.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. The auditor need not focus on factors that are objective and not susceptible to bias, since estimates based on such assumptions are less likely to be misstated.
If management (of a governmental body) declines to present supplementary information required by the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB), the auditor should issue a(an):
Choice 'd' is correct. If management (of a governmental body) declines to present information required by the GASB, the auditor should issue an unqualified opinion with an additional explanatory paragraph.
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'c' are incorrect, per the above Explanation: .
An auditor observes the mailing of monthly statements to a client's customers and reviews evidence of follow-up on errors reported by the customers. This test of controls most likely is performed to support management's financial statement assertions of:
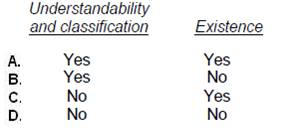
Choice 'c' is correct. In testing the existence or occurrence assertion, the auditor is concerned that fictitious or overstated receivables may have been recorded. Observing the mailing of monthly statements and reviewing evidence of follow-up on errors reported by customers provides evidence that procedures are in place to identify and correct such errors.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Follow up of errors in monthly statements does not provide any evidence to support understandability and classification.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Follow up of errors in monthly statements does not provide any evidence to support understandability and classification, but does provide evidence regarding the existence of receivables.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. Follow up of errors in monthly statements does provide evidence regarding the existence of receivables, since customers will be likely to report discrepancies.